Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “clearance”
clearance: shortest distance in air between two conductive parts or between a conductive part and the
accessible surface.
Clearance is a very important concept. In order to understand clearance, we need to say it again that no substance is completely insulated, and air can also conduct electricity. When the voltage is very high, the current will be conducted through the air. The lightning strike during thunderstorms is a typical example of lightning conducting through the air. The voltage of lightning is very high, so it can break through a very long section of air, making this section of air conductive. In household electrical appliances, although the voltage is very low, there is a lot of air in the product, and current will also be conducted through the air. As the voltage increases, the distance that the voltage may break through the air will also become longer. This gives rise to the concept of clearance.
For a detailed explanation of clearance, please refer to IEC 60664-1 (Insulation coordination for equipment within low-voltage systems – Part 1: Principles, requirements and tests).
I think the following pictures can well explain the path of electrical clearance.
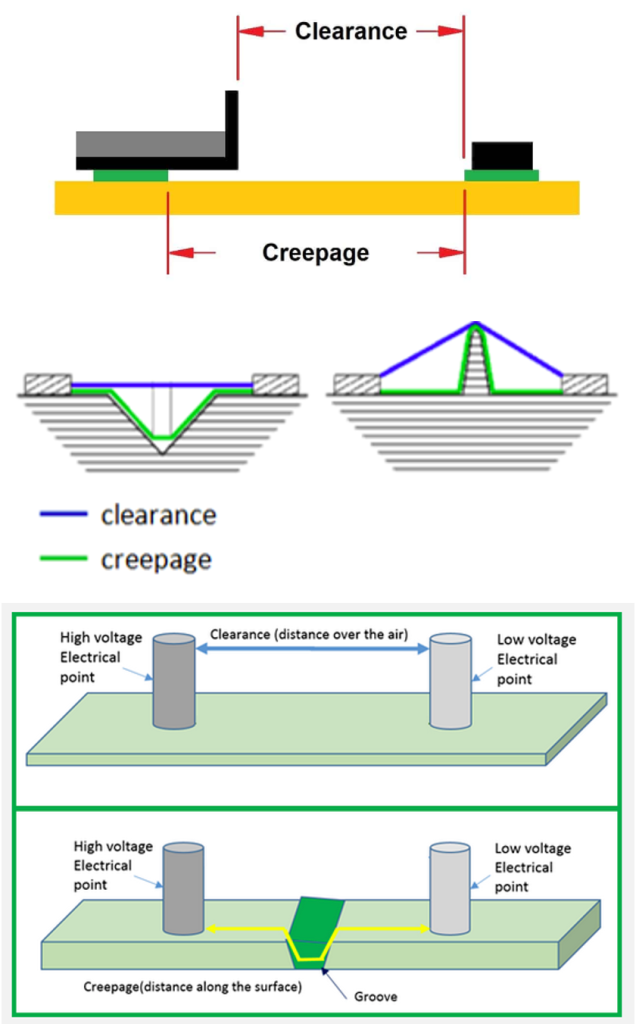
A clearance can be formed between two electrodes of different voltages, or between a live part and the hand of an electrical product user. You just need to imagine the two electrodes in the picture above as other objects.
When we explained basic insulation and functional insulation, we gave some real photos to explain the examples of clearance and creepage.
Figure 11 – Examples of clearances in the IEC 60335-1 standard gives a simple example. Based on this figure, we can think about the basic characteristics of class II appliance, class II construction, class I appliance, and class I construction.
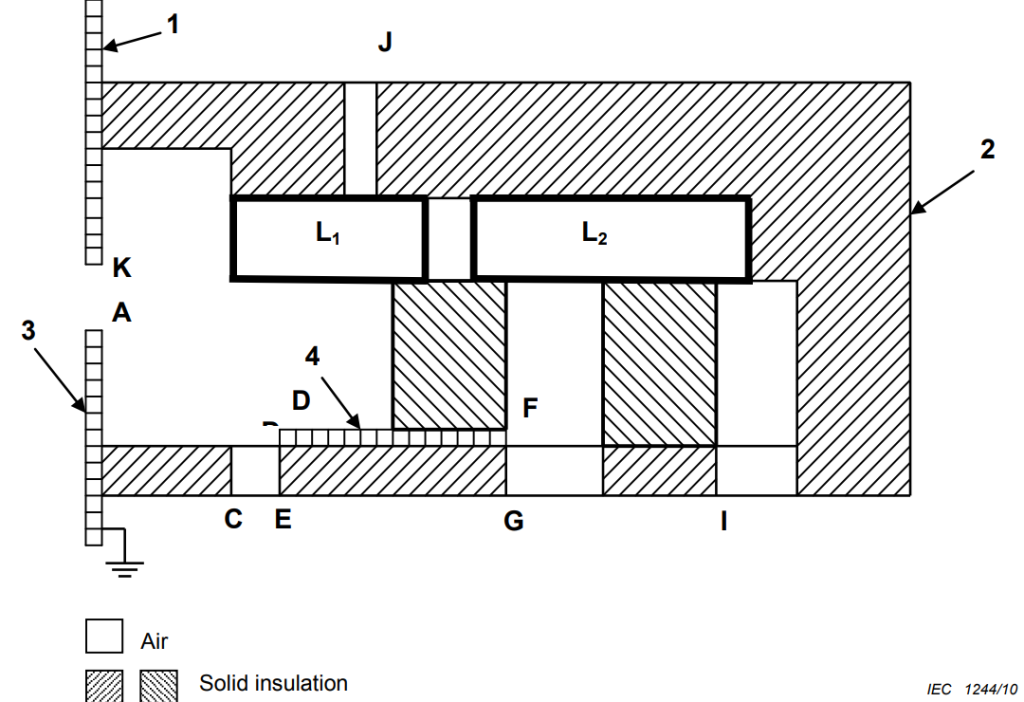
Key
1 accessible unearthed metal part
2 enclosure
3 accessible earthed metal part
4 inaccessible unearthed metal part
The live parts L1 and L2 are separated from each other and partially surrounded by a plastic enclosure containing apertures, partially by air and are in contact with solid insulation. A piece of inaccessible metal is incorporated inside the construction. There are two metal covers, one of which is earthed.
Type of insulation Clearance
Basic insulation L1A
L1D
L2F
Functional insulation L1L2
supplementary insulation DE
FG
reinforced insulation L1K
L1J
L2I
L1C
NOTE If the clearances L1D or L2F meet the clearance requirements for reinforced insulation, the clearances DE or FG of supplementary insulation are not measured.