Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “safety isolating transformer”
safety isolating transformer: transformer, the input winding of which is electrically separated from the output winding by an insulation at least equivalent to double insulation or reinforced insulation, that is intended to supply an appliance or circuit at safety extra-low voltage
The transformer mentioned here is used to supply power to appliances or circuits. Most common transformers supply power to circuits, and a few supply power to appliances. The key here is the isolation measures of the input winding and the output winding, which need to be double insulation or reinforced insulation type, or equivalent type of insulation. This requirement is to ensure that the primary winding and the secondary winding have sufficient insulation. If the insulation is sufficient, the isolation between the primary and secondary windings of the transformer is relatively safe. Double protection precautions.
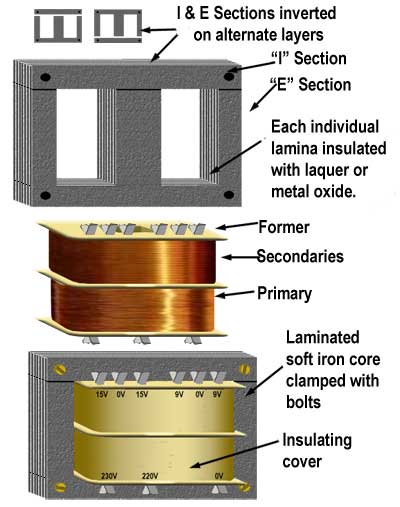
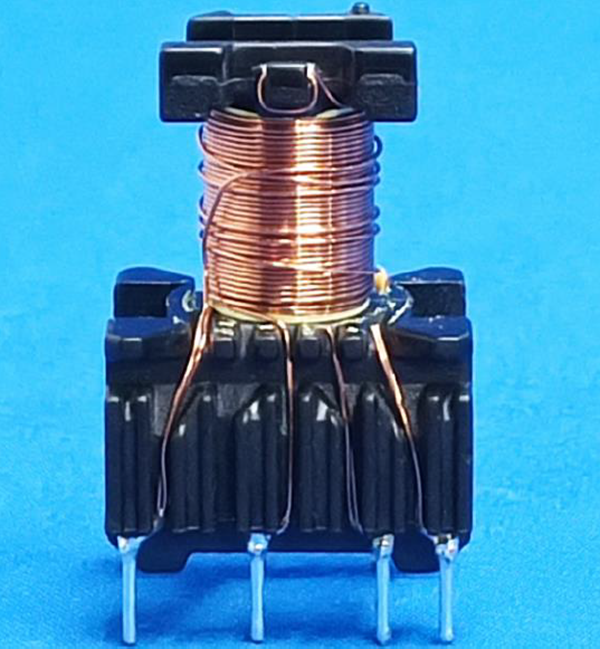
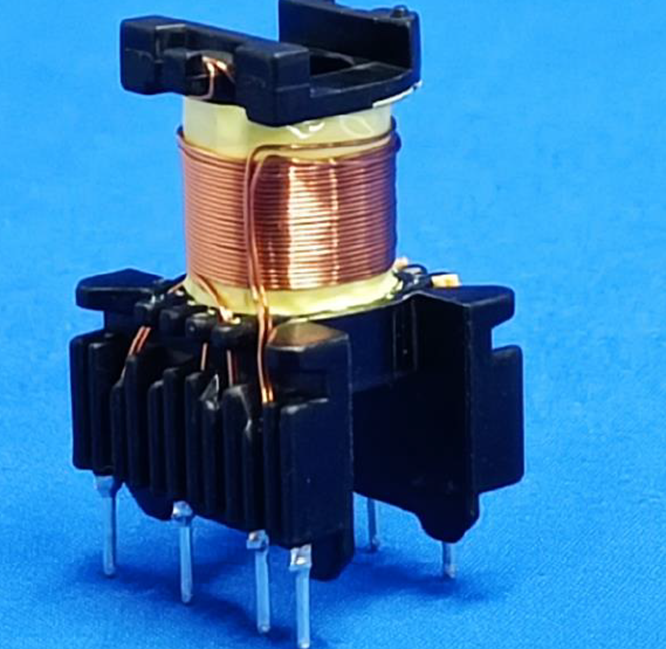
The two most commonly used transformers in household appliances are shown in the figure below.
The first kind of transformer used in the switch power supply PCBboard. This type of transformer will superimpose the primary and secondary windings on the same magnetic core. Therefore, in order to ensure the creepage distance and electrical clearance between the primary and secondary, the wound windings cannot be placed on the upper and lower end faces. The windings need to be at a certain distance from the upper and lower end faces, as shown in the figure below:
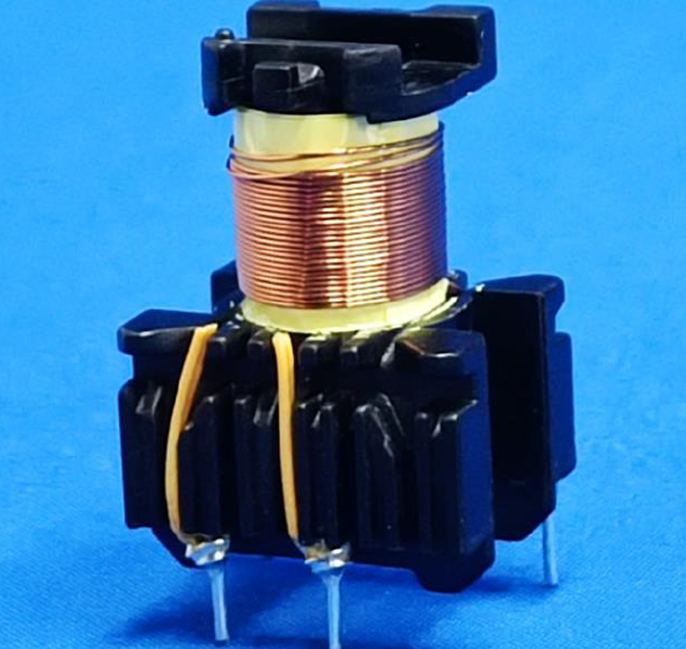
In order to help readers better understand the structure of this transformer, I have placed photos of the exterior and interior of the entire transformer on this page for readers’ reference.
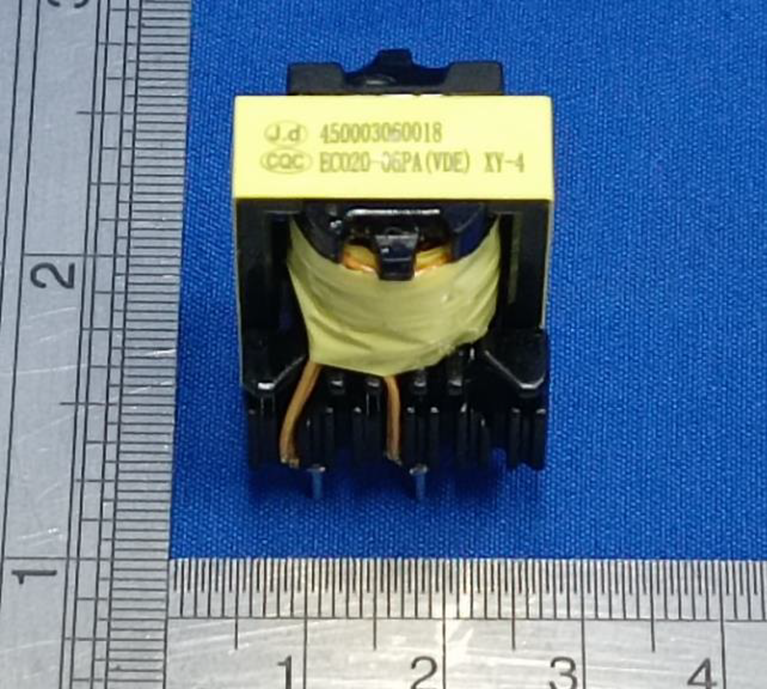

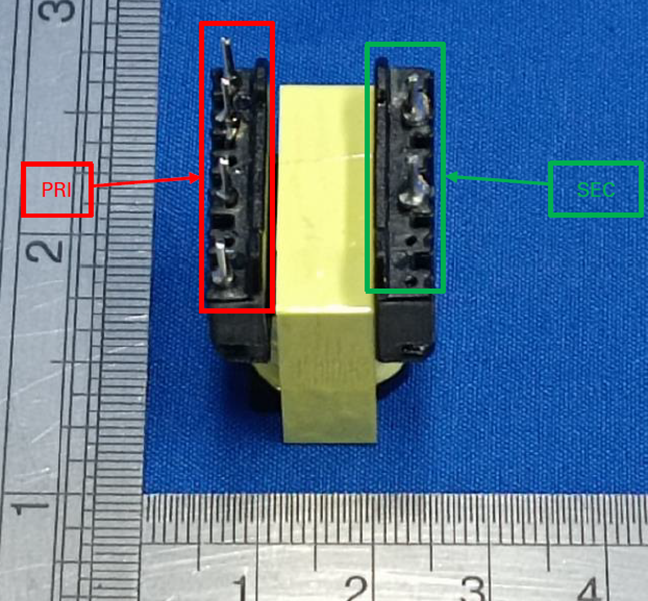
Overall view for safety insolating transformer
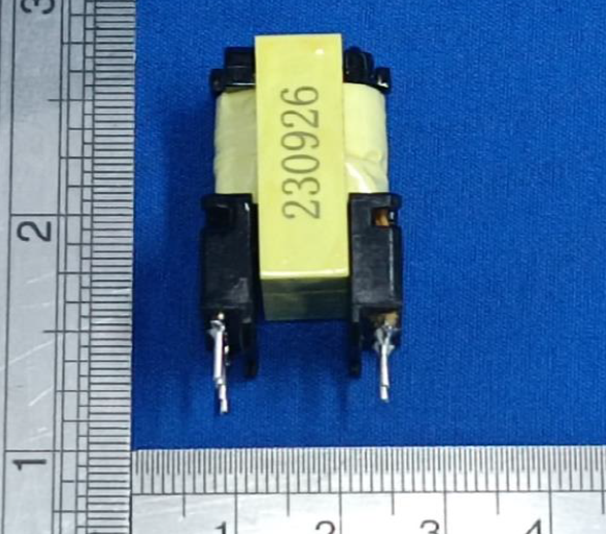

Overall view for safety insolating transformer
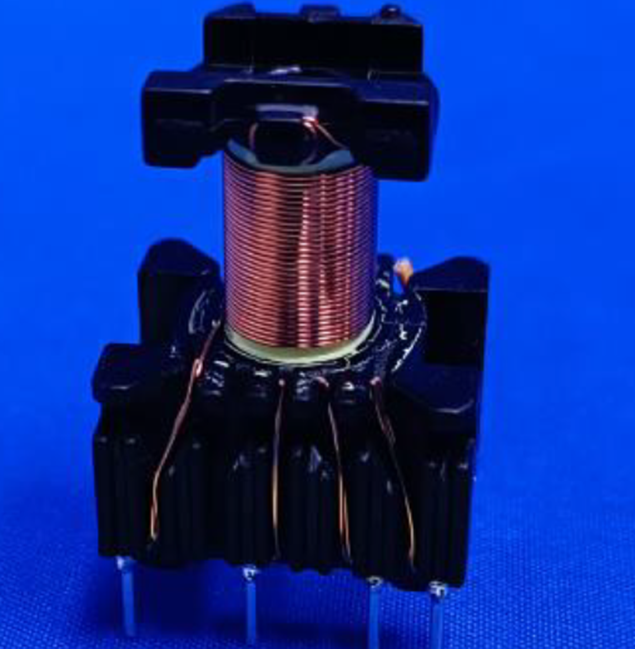
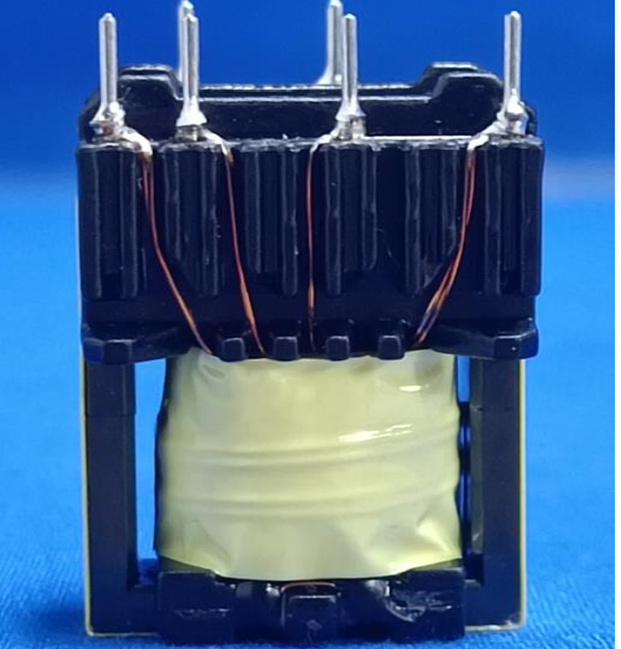


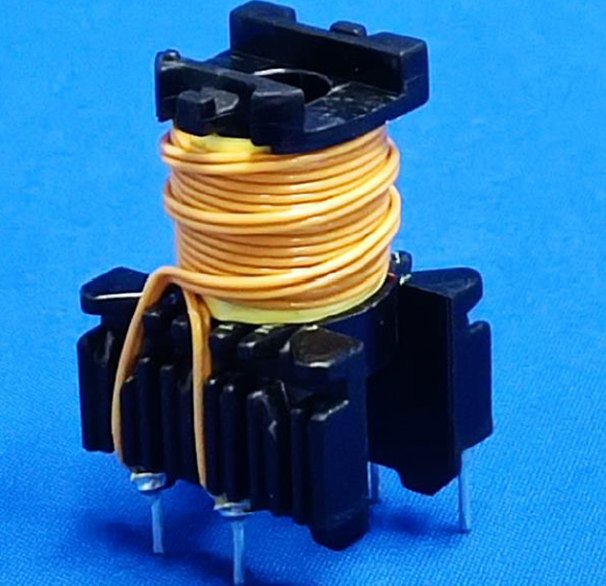


The other is a drawer-type linear transformer, as shown below: