Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “remote operation”
remote operation: control of an appliance by a command that can be initiated out of sight of the appliance using means such as telecommunications, sound controls or bus systems.
NOTE An infra-red control by itself is not considered one used for remote operation. However, it may be incorporated as part of a system such as a telecommunication, sound control or bus system.
From the content of the text is relatively easy to understand the meaning of this clause, here the communication system generally refers to the telephone line, only from the fourth edition of the standard began to have this definition, the reason is also because the standard is usually lagging behind the technology, in addition, the sound control is usually through the ordinary telephone line signals to achieve, the bus system generally refers to the use of communication protocols such as 485 bus control system. It should be noted that the definition of the control mode, is different from the field control, for field control, the user can observe the current operating state of the appliance; and remote operation, the controller is not in the vicinity of the appliance, can not be observed through the scene to know the working state of the appliance.
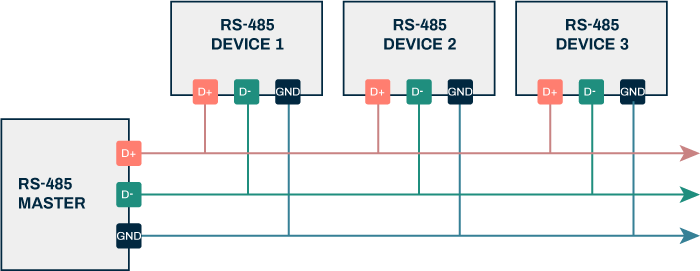
The author believes that the current commonly used WIFI remote control, 485 bus protocol mode control (such as the central air conditioning control system of some commercial buildings) and so on are a kind of remote control.

Commonly used infrared remote controls are not remote operation, because the user of the infrared remote controls is at the working site of the appliance, and can view the reaction and working status of the appliance after the infrared remote controls is operated in real time. If the infrared remote controls is part of a communication system, a sound control system or a bus system, in this case, the initiator of control mainly completes the control through the communication system, the sound control system or the bus system. Generally speaking, the initiator of control sends instructions to a separate infrared controller through the communication system, the sound control system or the bus system, and then the infrared controller transmits infrared remote control information to the appliance to complete the operation; in this case, this set of control systems can be considered as remote operation.
Example: The infrared remote controller used for ordinary air conditioners is not remote operation; there is a centralized controller on the market currently that can be placed in the core position of a building. Users can control it to transmit infrared signals through WIFI. The transmitted infrared signals can control any electrical products in the room. This is a remote operation.