Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “class II appliance”
class II appliance: appliance in which protection against electric shock does not rely on basic insulation only but in which additional safety precautions are provided, such as double insulation or reinforced insulation, there being no provision for protective earthing or reliance upon installation conditions.
NOTE 1 Such an appliance may be of one of the following types:
– an appliance having a durable and substantially continuous enclosure of insulating material which envelops all metal parts, with the exception of parts, such as nameplates, screws and rivets, which are isolated from live parts by insulation at least equivalent to reinforced insulation; such an appliance is called an insulationencased class II appliance;
– an appliance having a substantially continuous metal enclosure, in which double insulation or reinforced insulation is used throughout; such an appliance is called a metal-encased class II appliance;
– an appliance which is a combination of an insulation-encased class II appliance and a metal-encased class II appliance.
NOTE 2 The enclosure of an insulation-encased class II appliance may form a part or the whole of the supplementary insulation or of the reinforced insulation.
Here we think from the perspective of double precautions. In addition to basic insulation, the product also needs another layer of insulation, that is, double insulation measures to ensure that if any layer of insulation fails, there will be another layer of insulation to still play a protective role. The anti-electric shock effect of reinforced insulation is equivalent to double insulation in most cases, so it is also considered to be an effective way of double precautions. Class II appliances defined by the standard mainly emphasize that the appliance achieves the effect of double insulations through its own casing, insulated wires, and sheaths of insulated wires. Appliances with earthing measures are Class I appliances, so Class II appliances do not have protective earthing.
Except for Class 0 appliances, all appliances with large area plastic or insulating housings are generally designed as Class II appliances. However, there are also some motors with a metal housing, although the product can meet the requirements of Class II appliances, there is still a protective earthing measure on the motor. This appliance is considered a class I appliance. The notes to this clause give an introduction to the structural features of all possible Class II appliances.
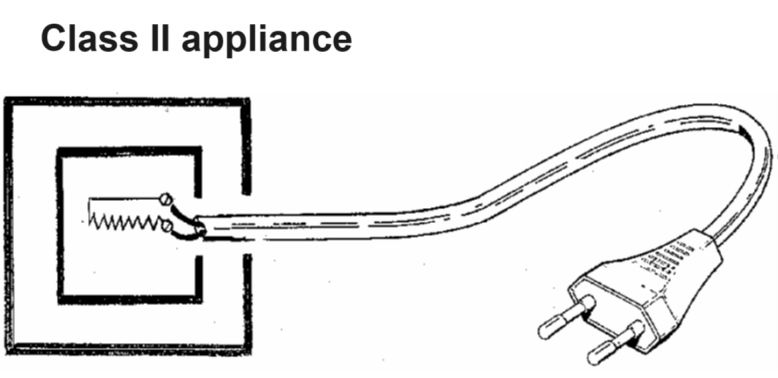
Figure 11 – Examples of clearances in the IEC 60335-1 standard gives a simple example. Based on this figure, we can think about the basic characteristics of class II appliance, class II construction, class I appliance, and class I construction.