Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “extra-low voltage”
extra-low voltage: voltage supplied from a source within the appliance that does not exceed 50 V between conductors and between conductors and earth when the appliance is supplied at rated voltage
According to the definition of the EU Low Voltage Directive, low voltage ranges from 50-1000V for AC and 75-1500V for DC. By the way, most countries divide high and low voltages according to this voltage value. Therefore, voltages above the upper limit of the range are high voltages, and voltages below the lower limit of the range are extra-low voltages. The definition here in the standard does not distinguish between DC and AC. Please note that here only a voltage name is defined according to the voltage value, and it does not define a certain part of the low-voltage circuit. Because voltage is relative, when measuring voltage, the voltage must be measured between the two ends, that is, the voltage needs to have a reference point, so the standard mentions the voltage between the wires and between the wires and the ground.
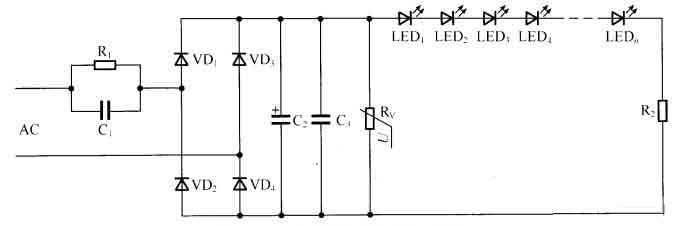
The output voltage of ordinary household alkaline batteries, the working voltage of the low-voltage circuit after the transformer or the RC step-down circuit on the control circuit board of ordinary household appliances, all of which can be defined as extra-low voltage.
As shown in the figure below, R1 and C1 complete a voltage reduction function, so the circuit following R1 and C1 can be defined as an extra-low voltage circuit.