Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “heating appliance”
heating appliance: appliance incorporating heating elements but without any motor.
Before introducing this definition, we need to briefly introduce the electric heating elements commonly used in household electrical appliances.
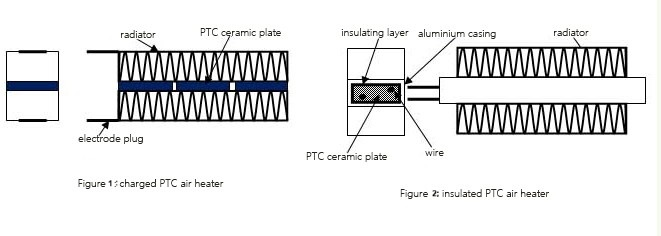
PTC heating element: PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) heating elements are widely used for various heating applications because of their self-regulating properties and safety features. Here are the key characteristics:
1. Self-Regulating Function
Automatic temperature control: As the temperature increases, the electrical resistance of the PTC material increases, which reduces the current flowing through it. This effectively limits the temperature rise, making the element self-regulating.
No external control required: PTC heaters can automatically limit their maximum operating temperature, so there is no need for complex control systems.
2. Temperature Coefficient
Positive Temperature Coefficient: The resistance of the PTC element increases as the temperature rises. This characteristic is different from typical conductors, where resistance remains relatively constant.
Non-linear resistance curve: There is a sharp increase in resistance after a certain temperature, known as the “Curie temperature,” which makes the element stop drawing more current and maintain its set point.
3. Safety
Overheating protection: Due to the self-regulating behavior, PTC heaters are less prone to overheating, making them inherently safer for many applications.
Fail-safe operation: If airflow is blocked or there’s insufficient heat dissipation, the element will not overheat dangerously but rather reduce its power output.
4. Durability and Longevity
Long lifespan: The absence of moving parts and the self-regulating property means PTC heating elements tend to last longer than traditional resistive heaters.
Low maintenance: Since there are no parts that wear out easily, PTC elements typically require minimal maintenance.
5. Energy Efficiency
Efficient energy usage: By adjusting the power consumption automatically based on the surrounding temperature, PTC heaters only draw the necessary amount of power, reducing wasted energy.
Faster heat-up times: PTC elements can heat up quickly to a stable temperature and maintain it efficiently.
6. Wide Range of Applications
Versatile: PTC heaters are used in a variety of industries and products, including space heaters, car seat heaters, defrost systems, and industrial heating equipment.
Compact: They are available in various forms, including ceramic, polymer, and metal components, making them suitable for small, portable applications.
7. Electrical Insulation
Excellent insulation properties: Many PTC materials provide good electrical insulation, reducing the risk of electrical faults and ensuring safe operation in environments where exposure to moisture or other conductive elements is possible.
8. Constant Temperature Maintenance
Stable operating temperature: Once the element reaches a specific temperature, it will stay close to that temperature without the need for external thermostats or controllers.
9. Design Flexibility
Custom shapes and sizes: PTC elements can be made in different shapes and sizes to suit specific applications, from small-scale heating pads to large-area heaters.
These characteristics make PTC heating elements particularly advantageous for use in products requiring safe, efficient, and low-maintenance heating solutions.
PTC heating elements are typically used in HVAC products.

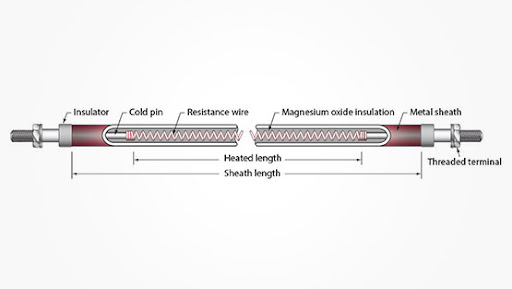
Electric heating tubes, also known as electric heating elements or tubular heaters, are devices used for heating through electrical resistance. They consist of a resistive wire encased in a metal tube and are commonly used in industrial and household heating applications. Here are the key characteristics:
1. High Efficiency in Heat Transfer
Direct heat transfer: Electric heating tubes convert almost all the electrical energy into heat with minimal energy loss. The heat is transferred directly to the medium (air, water, oil, etc.) that needs to be heated.
Uniform heating: The heat is evenly distributed across the surface of the heating element, leading to uniform temperature control.
2. Durable Construction
Robust metal tube: The heating wire is encased in a metallic sheath, usually made from materials like stainless steel, Incoloy, or copper, which are corrosion-resistant and capable of withstanding high temperatures.
Long lifespan: Due to their strong construction and efficient heat dissipation, electric heating tubes are known for their long operational life.
3. Insulation Material
Magnesium oxide (MgO) powder: The heating wire inside the tube is insulated by compacted magnesium oxide powder, which offers excellent thermal conductivity while providing electrical insulation to prevent short circuits.
4. Fast Heating Response
Quick temperature rise: Electric heating tubes can reach their operating temperatures quickly due to the efficient resistance heating of the wire inside. This allows them to deliver heat rapidly to the medium.
5. Versatility in Applications
Multiple forms and shapes: Electric heating tubes can be manufactured in various shapes, such as straight, U-shaped, or coiled, to meet the requirements of different applications.
Wide range of heating applications: They are used in industrial ovens, water heaters, oil heaters, boilers, kitchen appliances, air conditioners, and other heating systems.
6. Wide Temperature Range
High-temperature operation: Depending on the material used, electric heating tubes can operate at temperatures up to 800°C (1472°F) or more.
Stable temperature control: These heaters provide consistent heat over time, which makes them suitable for both low and high-temperature applications.
7. Easy Installation and Maintenance
Simple to install: They can be easily integrated into heating systems with minimal space requirements. The installation process is straightforward, and they can be replaced without major system overhauls.
Low maintenance: Electric heating tubes have no moving parts, which reduces wear and tear, resulting in minimal maintenance needs.
8. Energy Efficiency
Low energy loss: Since electric heating tubes convert nearly all electrical energy into heat, they are highly energy-efficient.
Low operating cost: Their efficiency translates into lower operating costs over time, especially when compared to traditional heating methods like gas or combustion heaters.
9. Corrosion and Environmental Resistance
Corrosion resistance: The metallic sheath of the heating tube, often made of stainless steel or Incoloy, makes it resistant to corrosion, especially in applications involving liquids, such as water heaters or oil baths.
Resistant to harsh environments: Electric heating tubes can be used in environments exposed to chemicals, humidity, and pressure, depending on the materials used in their construction.
10. Safety Features
Thermal insulation: The insulation materials inside the tube provide protection against electrical leakage and ensure safe operation.
Explosion-proof designs: In some applications, electric heating tubes can be designed with explosion-proof characteristics for use in hazardous environments.
11. Customizability
Custom wattage and voltage: Electric heating tubes can be designed to operate at different power levels (wattage) and voltage requirements, making them suitable for a variety of industrial and domestic needs.
Shape and size flexibility: The design flexibility allows manufacturers to tailor electric heating tubes for specific heating applications (like immersion heaters, cartridge heaters, or finned tubular heaters for air heating).
12. Applications
Domestic uses: Common in water heaters, ovens, toasters, dishwashers, and space heaters.
Industrial uses: Widely used in chemical processing, oil heating, HVAC systems, boilers, and industrial furnaces.
13. Cost-Effectiveness
Affordable production: Due to their relatively simple design and common materials, electric heating tubes are cost-effective compared to other advanced heating technologies.
Low operating cost: Their high energy efficiency means lower electricity consumption over time, making them economical for long-term operation.
These characteristics make electric heating tubes ideal for applications where reliable, efficient, and controlled heating is essential, both in industrial processes and household appliances.
This type of heating tube is used in a wide range of applications such as ovens, room heaters, kettles, etc.

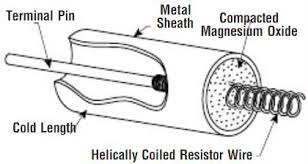
Electric heating wire:
The spring-shaped electric heating wire in the electric furnace shown below, their material is usually ferrochrome-aluminum alloy: electric heating wire made of this material has the advantages of high resistivity, long life at high temperatures, light weight, and inexpensive. Especially suitable for use in the atmosphere containing sulfur and sulfide, it is the ideal heating material in industrial electric furnaces, household appliances, infrared heating devices. Iron-chromium-aluminum alloy can be used up to a maximum temperature of 1400 ℃, with excellent high-temperature oxidation resistance. However, the disadvantage of iron chrome aluminum alloy is the low high-temperature strength, with the use of temperature increases its plasticity increases, the components are easy to deform, not easy to bend and repair.
This heating material is used in many types of products, such as heated stoves for kitchens, room heaters, etc.

There are also some electric ceramic stoves and electric blankets that use carbon heating materials, which are characterized by fast heat generation, long heat radiation transmission distance, even heat generation and long life.
There are several kinds of heating materials as follows
Graphene: Graphene is a new type of two-dimensional carbon nanomaterials, with excellent thermal conductivity and electric heat conversion efficiency. Graphene electric blanket can rapidly generate heat and improve the warming and insulation effect.
Carbon nanotube film: This is a new type of flexible heating material, composed of hexagonally arranged carbon atoms forming a single layer to dozens of layers of coaxial tubes, with excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, long service life, belonging to the surface heat, heat uniformity.
Nickel-chromium alloy: nickel-chromium alloy electric heating wire main chemical composition of nickel and chromium, has a high electrical resistivity, good surface oxidation resistance, high thermal emissivity, corrosion resistance, resistance to vibration in the hot state, and has a high high-temperature strength, good processing performance and weldability. This material is made of electric heating wire high temperature strength than iron chromium aluminum alloy, high temperature use is not easy to deform, its structure is not easy to change, better plasticity, easy to repair. However, due to the use of scarcer nickel metal materials made of nickel-chromium alloy electric heating wire price is usually several times higher than the ferro-chromium aluminum alloy, and the use of lower temperatures than ferro-chromium aluminum alloy.
Using an electromagnetic coil as the heating element, the principle of electromagnetic induction is utilized to heat the metal material.
Far infrared heating is a newer heating method that directly heats the inside of food through the penetration and resonance principle of far infrared rays.
The heating methods and materials will not be introduced one by one, if necessary, you can check through the search engine.
According to the standard definition, a product with a heating element but without a motor is a heating appliance, because the product only has a heating element, so its function is generally used for heating, such as room heaters for heating air, kettles for heating water, ovens for heating food and so on.
A microwave oven, which heats water molecules in food by means of microwaves generated by a magnetron, is not a heating appliance, which is explicitly defined as a motor-operated appliance in clause 5.101 of the IEC 60335-2-25 standard.