第3項 「相互接続コード」の定義の見方
接続コードが主電源に接続されていない。これらはアプライアンスの 2 つの部分の間に配置されます。コードは電気エネルギーをある部分から別の部分に伝導できます。相互接続コードの概念は、相互接続コードによって引き起こされる危険を軽減するためにここで定義されます。規格 25.23 および 25.24 では、相互接続コードの要件が規定されています。標準要件の観点から、この規格では主に、機器の外部コード、使用中に発生する可能性のある引っ張り、および電源コードが耐える可能性のあるその他の同様の使用条件が考慮されています。したがって、電源コード以外の外部からアクセス可能なコードのほとんどは相互接続コードとみなすことができます。注1は代表的な例です。
床置き型ミストファンは下図のように、上図の壁掛け型ミストファンとは構造が異なりますが、機能は同じです。床置き型ミストファンは一体構造ですが、ファンヘッドと下の水タンクを繋ぐコードが外側にあります(コードは真ん中の支柱を通します)。この種の接続については、相互接続コードでもあると著者は考えています。
下図に示すように、分割型壁掛け型エアコン室内機の表示基板と主制御基板間の一般的なリード線です。トップカバーを手で開けばリード線に触れることができますが、通常の使用中はリード線が機器の内部にあるため、相互接続コードとはみなされません。ただし、リードは依然として第 22.8 条の要件を満たす必要があります。
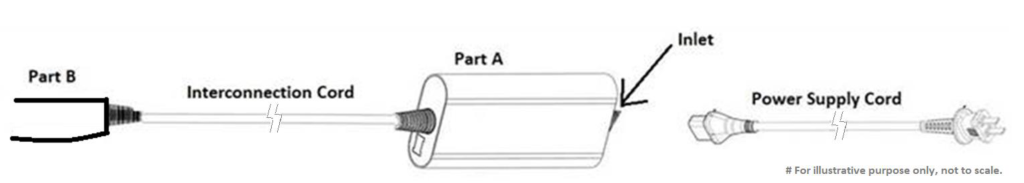
アプライアンスはコード セットによって供給され、パーツ A とパーツ B で構成されます。パーツ B は手持ち式で、相互接続コードによってパーツ A に接続されます。この情報は CTL 決定 OD-5002-F3:2021 に基づいています。
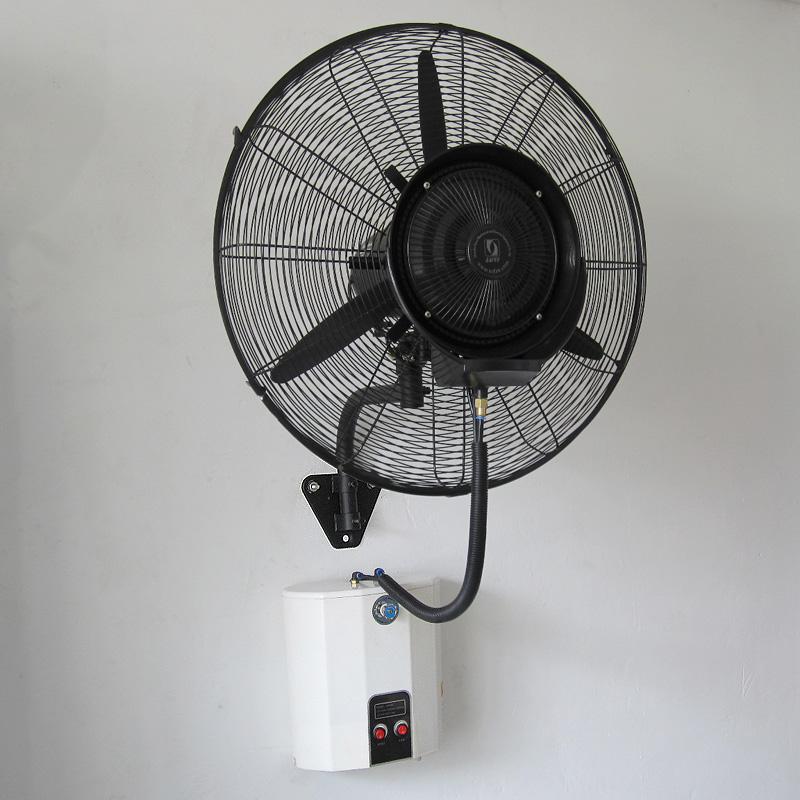

As shown in the figure below, a floor standing mist fan has a different structure from the wall mount mist fan shown in the figure above, but has the same function. The floor standing mist fan is an integral structure, but there is a cord outside connecting the fan head and the water tank below (the cord will pass through the middle support rod). For this kind of connection, the author believes that it is also an interconnection cords.

As shown in the figure below, this is a typical lead between the display circuit board and the main control circuit board of a split wall-mounted air conditioner indoor unit. Although the lead can be touched by manually opening the top cover, the lead is inside the appliance during normal use and is therefore not considered an interconnection cord. However, the lead still needs to meet the requirements of clause 22.8.

Here is a more controversial case, which is the cord inside the compressor compartment on the back of the refrigerator. The cord in the red circle in the figure below are considered to be interconnection cords by most third-party testing organizations or laboratories.

My personal opinion is that the cord in the refrigerator compressor compartment is not an interconnection cord. We can infer the intent of the standard from the requirements of 25.23 and 25.24. The standard requires that the interconnection cord needs to meet the requirements of the power cord. The power cord can be pulled, so the test of 25.15 is required. The power cord is characterized by being external to the appliance and can be touched and pulled. The refrigerator cord we are discussing here is unlikely to be touched and basically will not be pulled.
An appliance is supplied by a cord set and is composed of Part A and Part B, where Part B is handheld and connected to Part A by an interconnection cord. This information come from CTL decision OD-5002-F3:2021.