Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “small part”
small part: part, where each surface lies completely within a circle of 15 mm diameter, or a part where some of the surface lies outside a 15 mm diameter circle but in such a way that it is not possible to fit a circle of 8 mm diameter on any of the surfaces.
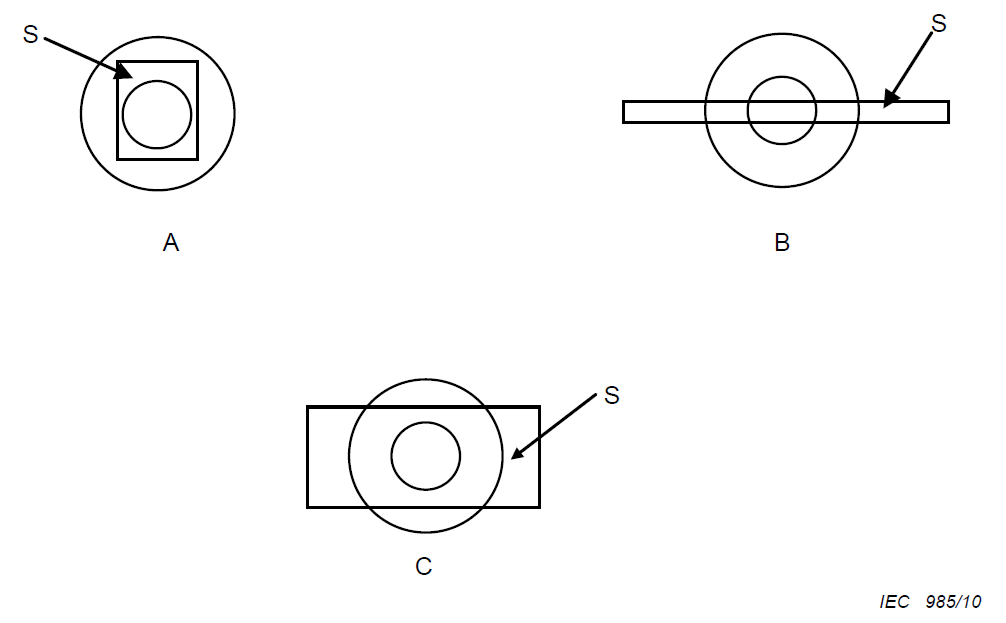
NOTE A part that is too small to grip and at the same time to be able to apply the glow-wire tip is shown in example A in Figure 5. A part that is large enough to grip but that is too small to be able to apply the glow-wire tip is shown in example B in Figure 5. A part that is not a small part is shown in example C in Figure 5.
The difference between small part and not a small part has been very well illustrated in Figure 5. Special attention should be paid here to the fact that every surface of the object needs to be considered when determining.

In the case of hollow structural members, or semi-hollow structural members, it is necessary to lay the parts out flat to make a determination.
A teat connector with a semi-hollow structure, as shown in the picture, is not a small part.
