Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “protective electronic circuit”
protective electronic circuit: electronic circuit that prevents a hazardous situation under abnormal operating conditions.
NOTE Parts of the circuit may also be used for functional purposes.
With the advancement of technology, more and more electronic circuits are being used in household electrical products, and these electronic circuits are usually integrated on PCBs. They use microprocessor chips and their burned-in programmes to complete the established functions, which include some regular operating functions and also some protective functions, which are defined as prevents a hazardous situation under abnormal operating conditions.
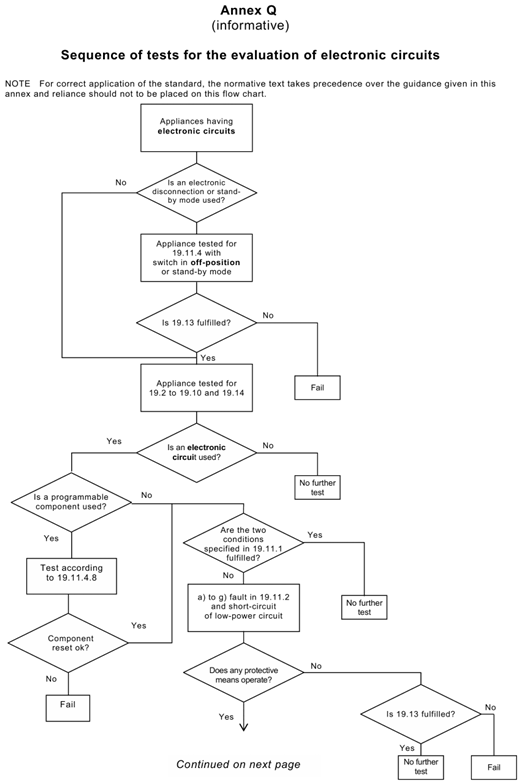
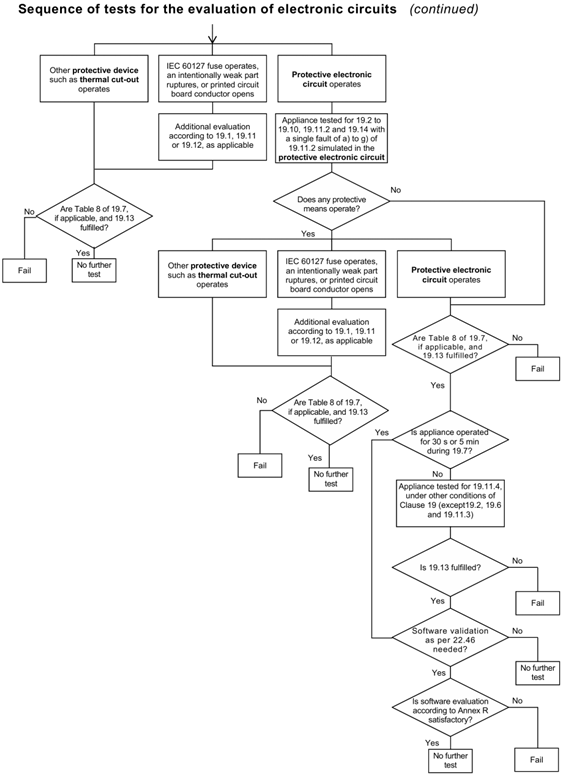
Generally speaking, it is difficult to distinguish which part of the circuit is protective electronic circuit, usually we will first carry out the abnormal test in clause 19, through the test phenomenon to determine whether there is an electronic circuit involved in the protective function, if there is, we need to find out which part of the circuit is protective electronic circuit according to the circuit schematic diagram and the test phenomenon. If so, we need to find out which part of the circuit is protective electronic circuit according to the schematic diagram and the test phenomenon, which requires analysts to have basic knowledge of circuits. Annex Q (informative) Sequence of tests for the evaluation of electronic circuits gives a flowchart for the evaluation of electronic circuits and protective electronic circuits. clearer.