Clause 3 – How to Understand the Definition of “all-pole disconnection”
all-pole disconnection: disconnection of both supply conductors by a single initiating action or, for multi-phase appliances, disconnection of all supply conductors by a single initiating action
NOTE For multi-phase appliances, the neutral conductor is not considered to be a supply conductor.
Single-phase power: An AC power system composed of one live wire and one neutral wire.
Three-phase power: An AC power system composed of three live wires, with the same frequency and a phase difference of 120 degrees between each.
Single-phase power has two poles, which are the live wire/pole and the neutral wire/pole, generally, when we refer to multi-phase power, it is typically Three-phase power. Three-phase power has two type of connection such ass Star connection (Y connection) and Delta connection (Δ connection).
Star connection (Y connection): In a Star connection (Y connection), one end of each of the three load supply leads is joined to form a common neutral point. The other ends are connected to the three live wires, respectively.
Delta connection (Δ connection): The three load supply power leads are connected end-to-end, forming a closed loop, with the connection points respectively connected to the three live wires.
The supply conductors mentioned in the standard refer to the live wire and neutral wire in single-phase power, as well as all conductors in three-phase power except the neutral wire in a star connection. Each conductor is defined as a pole or supply conductor.
A disconnection is considered all-pole disconnection if a single action simultaneously disconnects both the live and neutral wires in a single-phase power system, or all supply conductors in a three-phase power system.
The purpose of defining all-pole disconnection is to provide protection against electric shock. In single-phase systems, both neutral and live conductors are considered live parts. Similarly, in three-phase systems, all live conductors are considered live parts. As shown in the below pictures, it shows the three-phase power system and single-phase power system appliance, the temperature limiter shown in pictures is an all-pole disconnection.
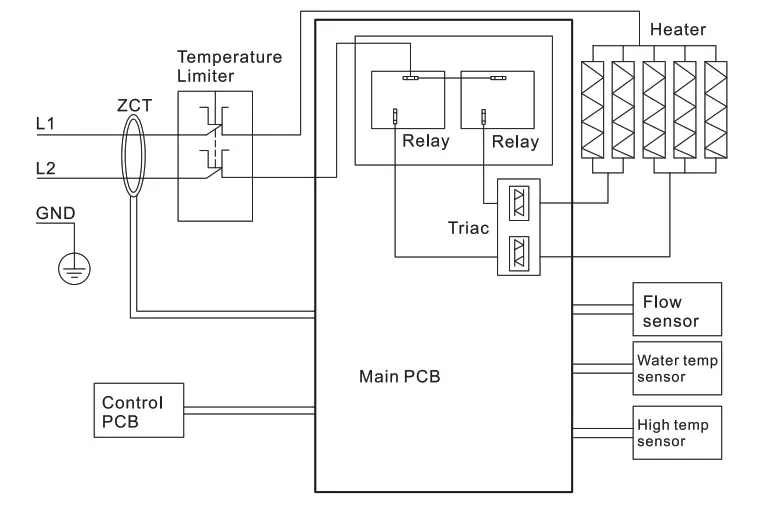
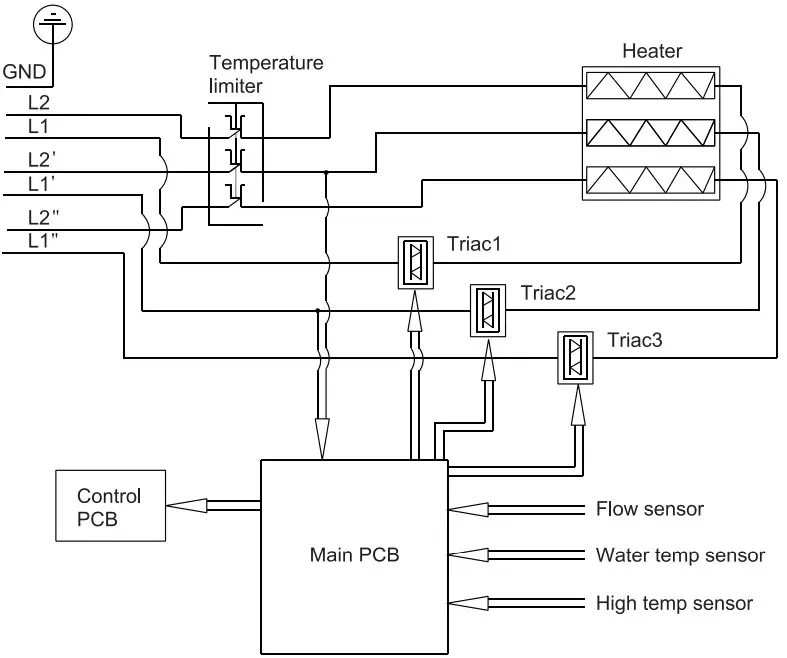
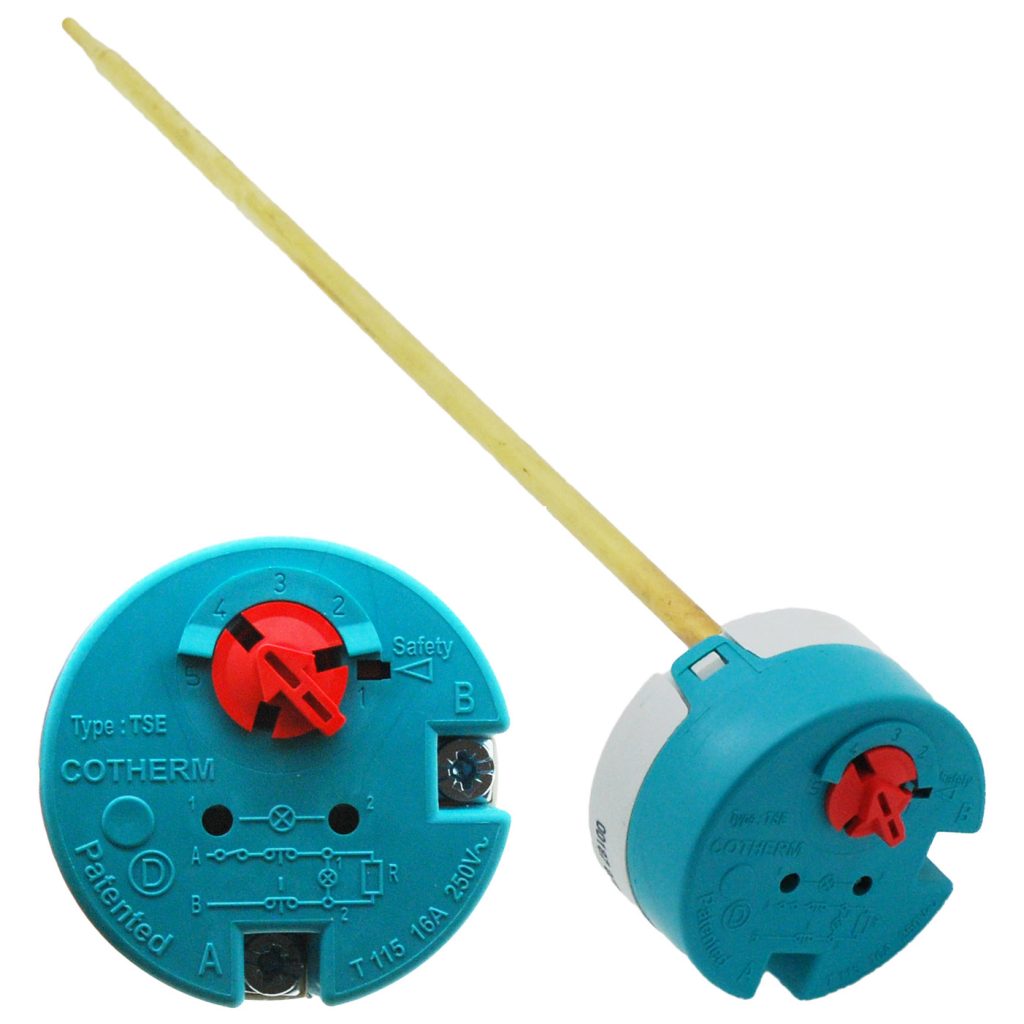
Below pictures show a thermal cut-out/ thermostat, you can find the all-pole disconnection diagram in its rating label.

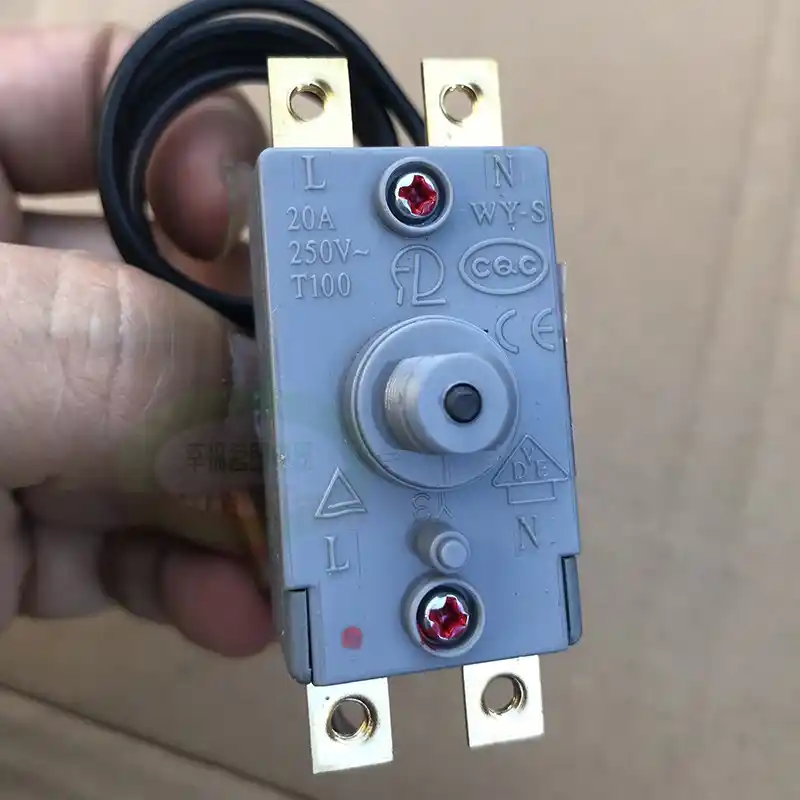
The bipolar thermal cut-out used in the kettle is shown in the figure below.
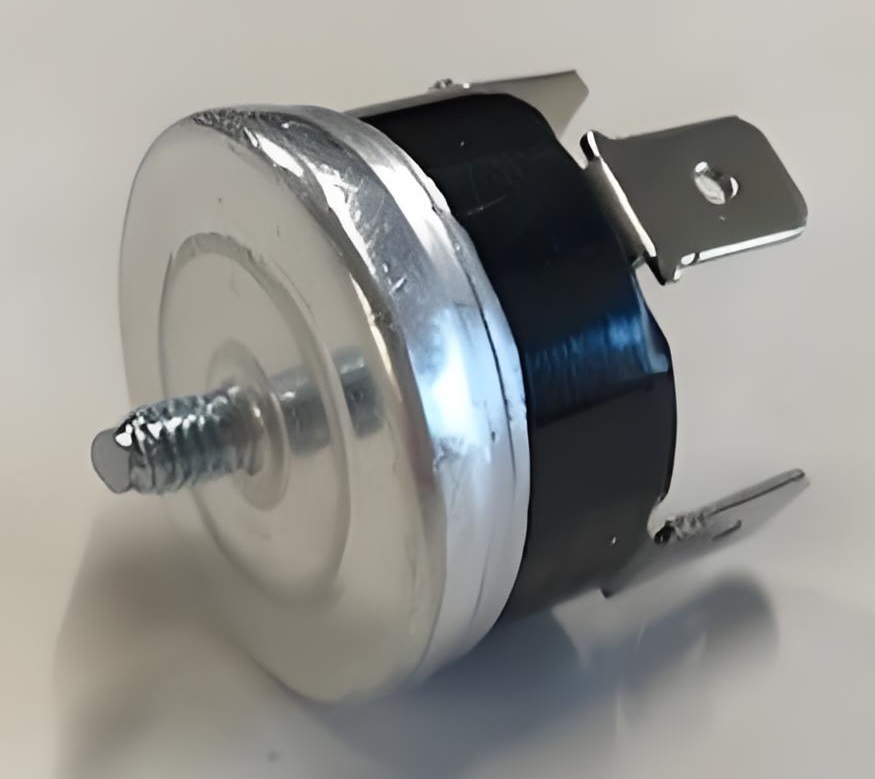


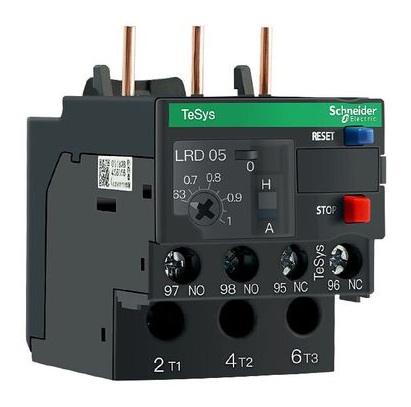
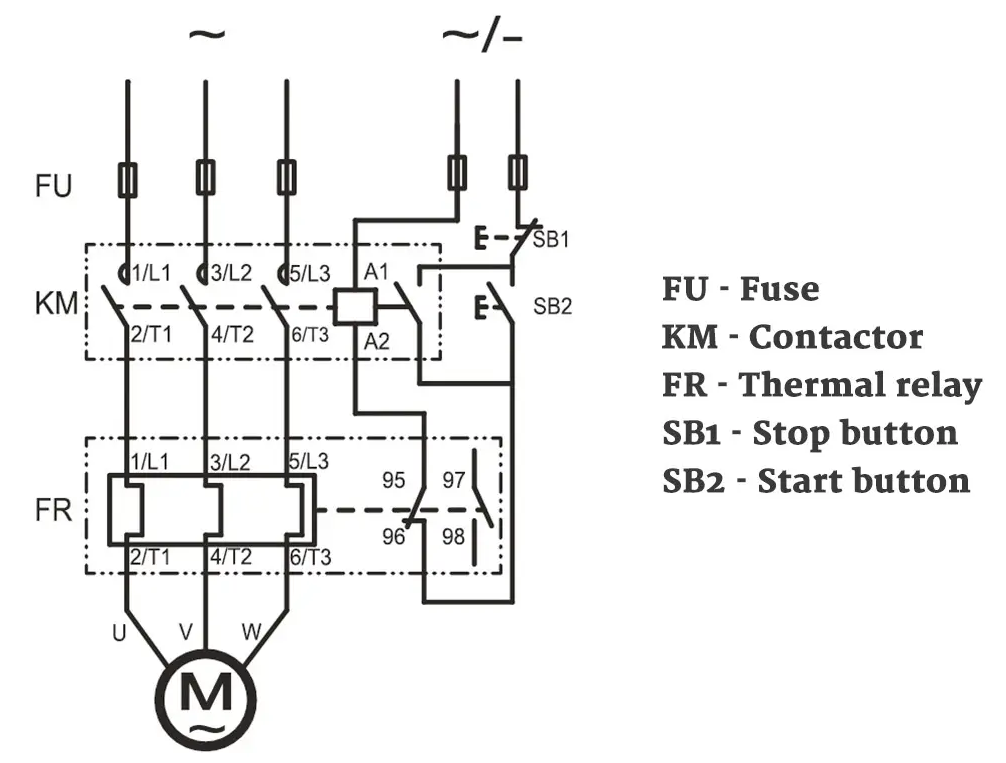
The diagram below shows a three-pole thermal overload relay, which is an example of an all-pole disconnection device.

The wire connection diagram and the picture of thermal protective devices used in water heaters with container are shown in pictures below:
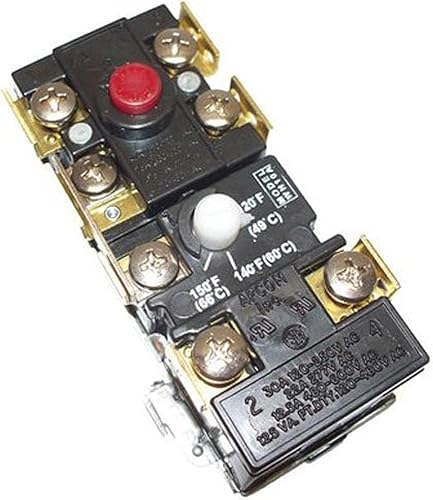
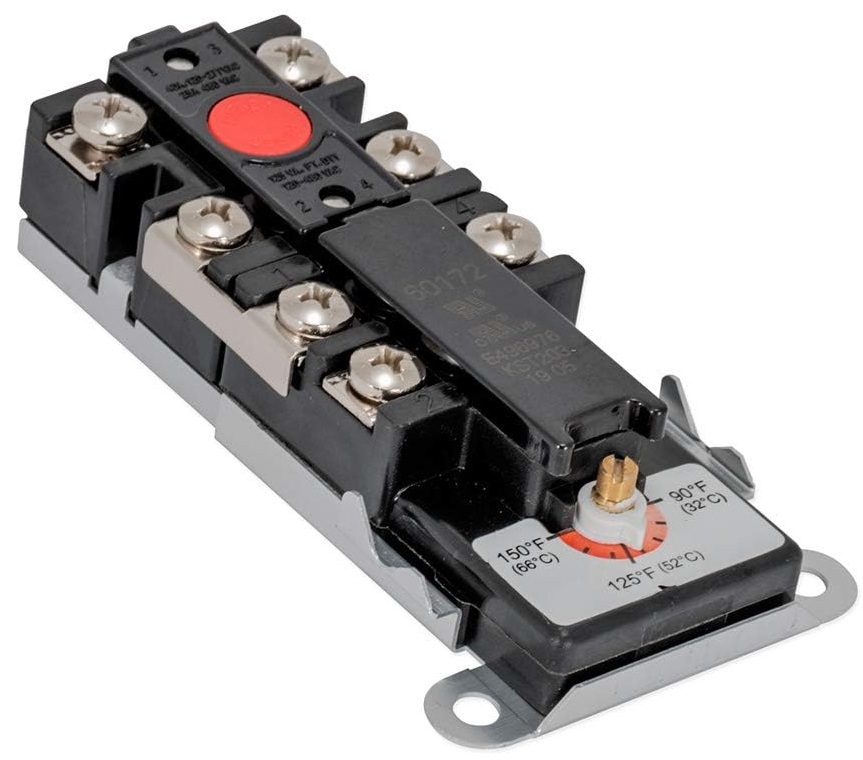


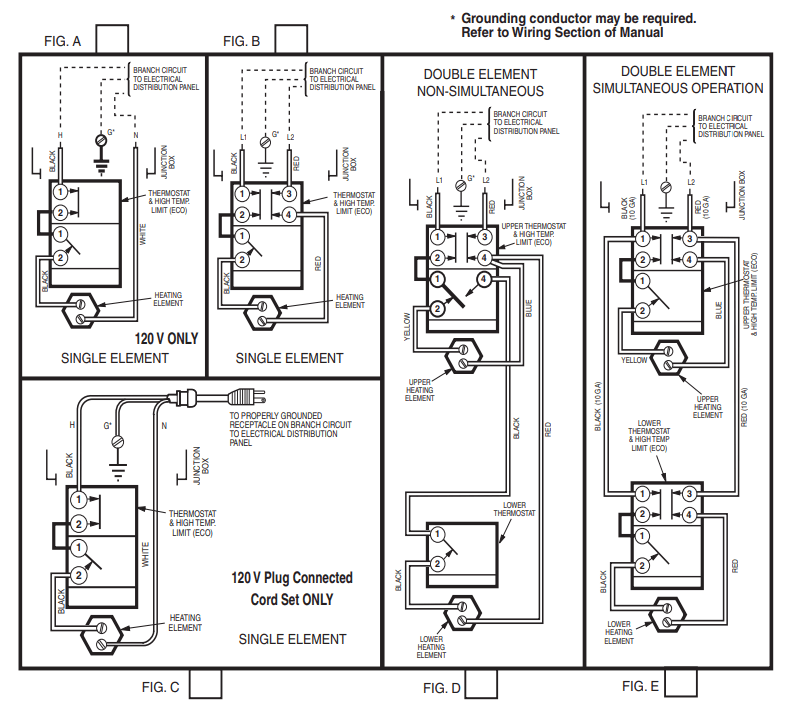
thermostat with temperature Adjustable one pole and 2-pole disconnection hand reset diagram.