Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “electronic component”
electronic component: part in which conduction is achieved principally by electrons moving through a vacuum, gas or semiconductor.
NOTE Neon indicators are not considered to be electronic components.
Early vacuum tubes were components that allowed electrons to conduct in a vacuum and were the core components of old radios and televisions.
Electrons move through specific gases, colliding with gas molecules and causing them to emit light or conduct electricity. Examples include plasma display screens.
Electrons move through semiconductor materials such as silicon and germanium, and their conductivity can be precisely controlled through doping, electric fields, and other methods. Examples include transistors, integrated circuits (chips), diodes, triodes, MOSFETs (metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors), and thermistors.
Note: “Neon indicator lights are not considered electronic components” is a very important qualification. Although neon lamps meet the definition of “electrons moving in a gas,” they are generally considered simple electric light sources.
The term “electronic component” generally refers to components (such as transistors and integrated circuits) that perform signal processing, control, and amplification functions in complex electronic circuits. Neon lamps are excluded because of their single function (indicating on/off) and simple structure.
Resistors, capacitors, and inductors are often referred to as passive components to distinguish them from active components (such as transistors and integrated circuits), which are not electronic components. Mechanical switches, thermostats, thermal cut-outs, pressure switches, motors, heating elements, batteries, and transformers are not electronic components.
This illustrates the subtle difference between theoretical and practical classifications.
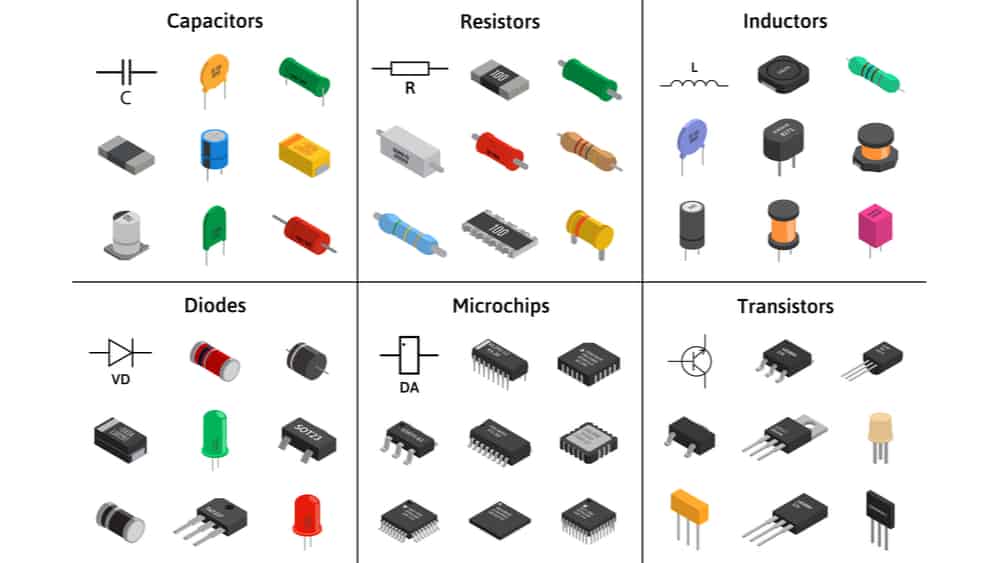
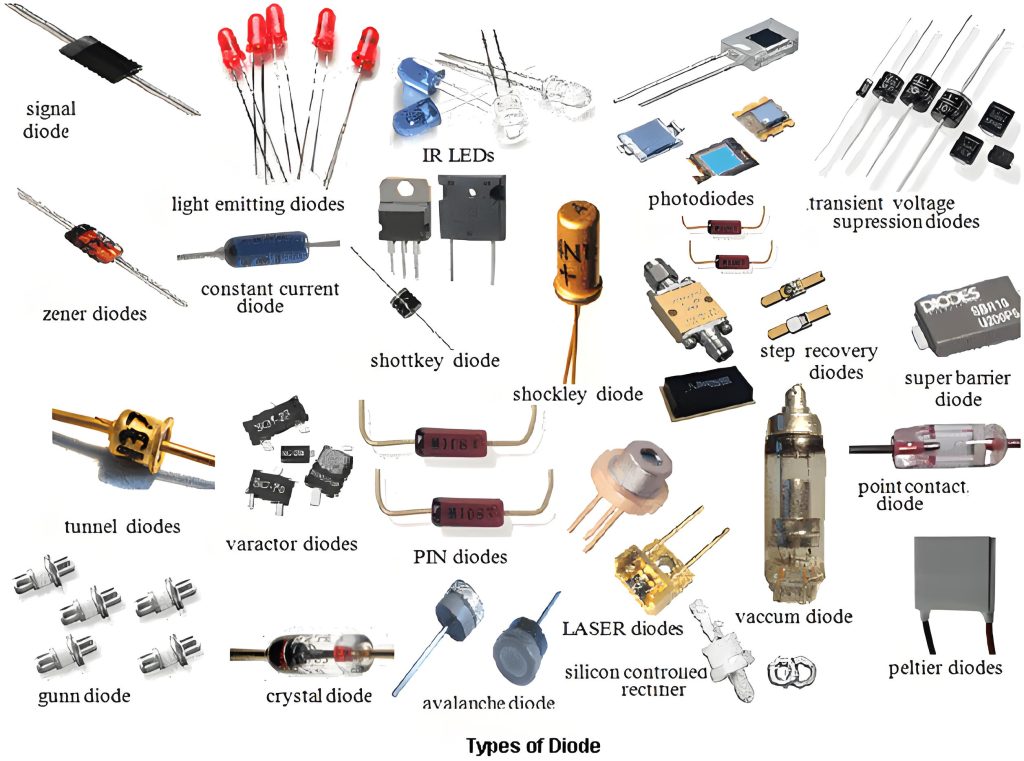
The main purpose of the definition of an electronic component is to show that electronic components are not completely reliable when they fulfil a protective function, but of course this unreliability is relative to non-electronic components.