Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “live part”
live part: conductor or conductive part intended to be energized in normal use, including a neutral conductor but, by convention, not a PEN conductor
NOTE 1 Parts, accessible or not, complying with 8.1.4 are not considered to be live parts.
NOTE 2 A PEN conductor is a protective earthed neutral conductor combining the functions of both a protective conductor and a neutral conductor.
In normal use (except abnormal use and for the protection of action) energized conductor and conductive parts. Conductor is easier to understand, as shown in the figure below, which is wrapped in copper conductor parts is live part.


The other part of the conductor that is energized can be a terminal, which can be an electrically powered component, such as a PTC heating element, a winding in a motor, a tungsten filament in a light bulb, a heating wire in a heating tube, and so on. Electrical products are energized in order to achieve the function for which they are designed, usually through the utility power supply. Normal utility power can cause electric shock, so the conductors in an appliance can be defined as live parts.
However, if the utility power is transformed to reduce the voltage, current and other values, then they may become conductors without electric shock damage. We know that ordinary household dry batteries are just no risk of electric shock, and some adapters, their outputs are just no risk of electric shock. For such conductors on circuits with low voltage and current, the standard considers them not to be live parts, but they need to be tested according to clause 8.1.4 of the standard to confirm whether they are live parts.
The conductor of the protective earthing is not a live part, but the neutral conductor is a live part, for example, in the following diagram of TN-S system, the conductors of A, B, C, N are all live parts, but PE (actually PEN) is not a live part, although we can see in the diagram that N and PE are connected together.
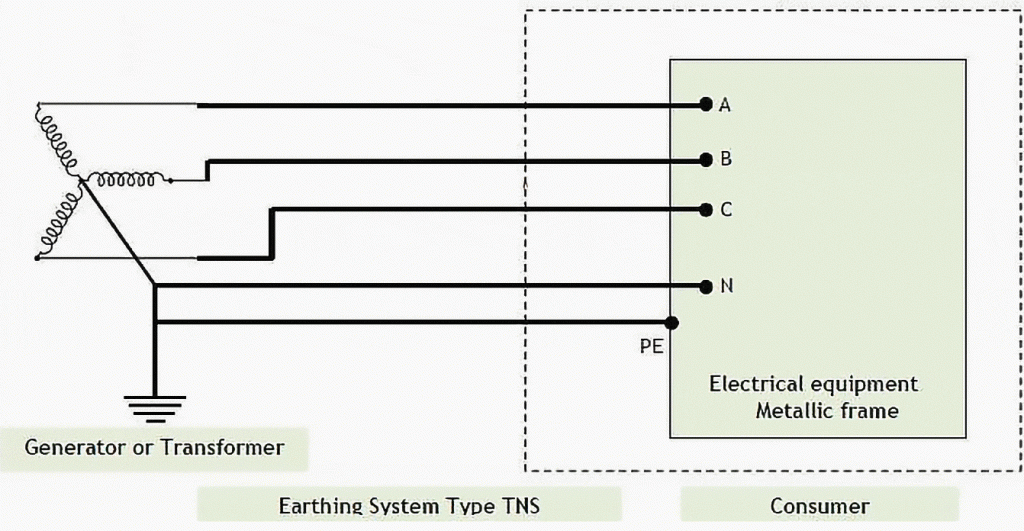
However, if the single-phase apparatus corresponds to the TN-S system, as follows
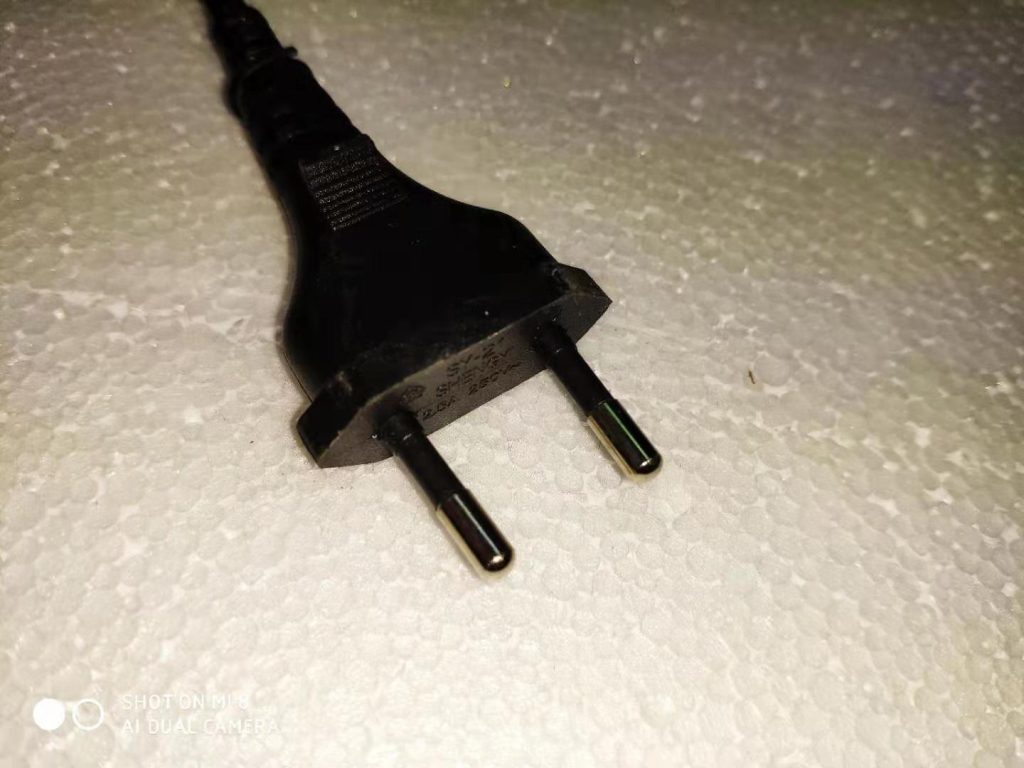
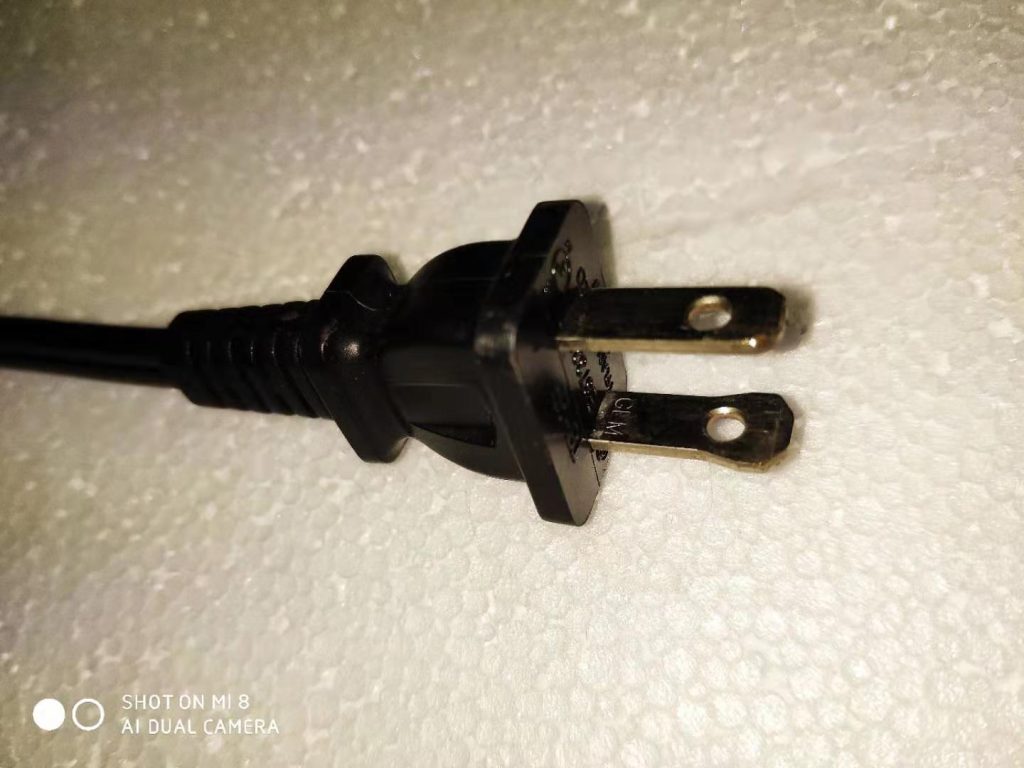
In many countries, while the socket-outlet can distinguish between L and N wires, the plug cannot distinguish between L and N wires, and therefore N is considered to be the Live part. the photo of the two plugs below illustrates the problem. The photo on the right is the plug with the polarity feature used in the US.

