Clause 3 – How to Understand the Definition of “off position”
off position: stable position of a switching device in which the circuit controlled by the switch is disconnected from its supply or, for electronic disconnection, the circuit is de-energized.
NOTE The off position does not imply an all-pole disconnection.
With reference to the content in the NOTE, both all-pole disconnection and single-pole disconnection are a stable condition of off position. So, what kind of electronic disconnection could be considered off position?
electronic disconnection, it could be achieved that the circuit is de-energized by relay, the circuit can also be disconnected by utilizing the switching function of a transistor, many other components capable of disconnecting circuits in a similar manner exist, though they will not be discussed here.
What we need to clarify is the difference between electronic disconnection and stand-by mode.
I checked standard IEC 335-1:1993 ED3.0, it gave us definitions below:
Off position: stable position of a switching device in which the circuit controlled by the switch is disconnected from its supply.
In the earlier version IEC 335-1:1976 ED2.0, the definition of “off position” was not yet established.
I searched the entire IEC 60335-1:2010+A1:2013+A2:2016 standard and found seven references to the “off position” within the document, like clause 7.10, clause 13.2, clause 16.2, clause 19.11, clause 19.13, clause 22.5, clause 22.55.
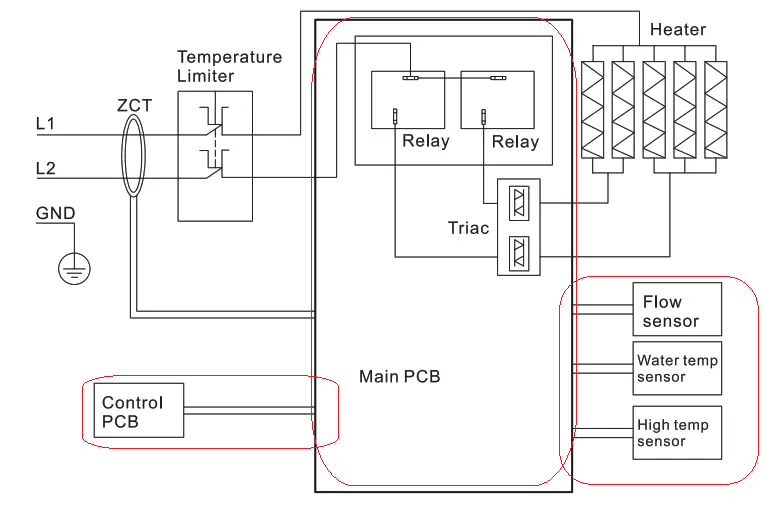
Particularly from the descriptions in clause 7.10 and clause 19.11, we can reasonably infer that electronic disconnection and stand-by mode should be considered as the off position. There is a word “circuit” in definition, it can be understood as the power supply circuit for the main energy-consuming components in the appliance, which excludes the electronic control circuits used for the PCB. As shown in the figure below, the content not highlighted by the red box corresponds to the “circuit” mentioned in the standard.