Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “user maintenance”
user maintenance: any maintenance operation stated in the instructions for use, or marked on the appliance, that the user is intended to perform.
Allowed user-executed operations, the operation guideline was given in user manual, and it could be showed in enclosure of appliance. Since it is a allowed user-executed operation, then additional protective method should be included in appliance to against hazards; moreover, we must consider that the user performing the maintenance operation does not have much experience with hazard protection, as well as reasonable misuse by the user during maintenance. We need to differentiate between maintenance and repairs; repairs are performed by professionals, and not much protection is needed for the repairers as they are more specialised.
Such as floor standing fan, usually the user will be allowed to disassemble and clean it, and the manual will give detailed instructions for disassembly and cleaning accordingly. A snippet of the instruction manual is shown below:
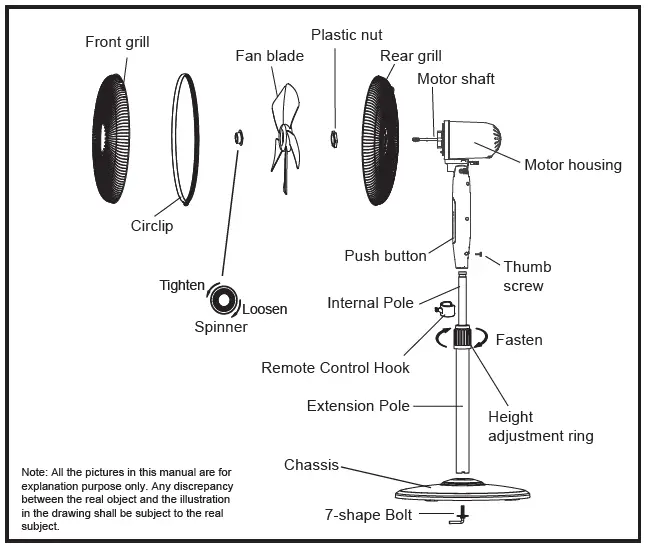
This is a typical type of user maintenance.
The standard refer to definition – user maintenance in clause 7.12, clause 15.1, clause 22.14, clause 23.3, and clause 28.1, which are primarily concerned with avoiding or minimising the hazards that can occur during user maintenance.