Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “thermal cut-out”
thermal-cut-out: device which during abnormal operation limits the temperature of the controlled part by automatically opening the circuit, or by reducing the current, and is constructed so that its setting cannot be altered by the user.
There are three key provisions here. First, the thermal cut-out is a heat-sensing element, second, it can only be actuated during abnormal operation, and third, it cannot be adjusted by the user. Meanwhile the definition mentions that its function is to limit the temperature, and it does so by opening the circuit or reducing the current. Usually, we would think that its function is to prevent the temperature from being too high, indeed, most of its function is to prevent the temperature from being too high; however, in my opinion it can also be used to prevent the temperature from being too low, for example, in refrigerators or air-conditioning products. However, when we look at the definition of self-resetting thermal cut-out, the standard actually wants to limit just the high temperature state.
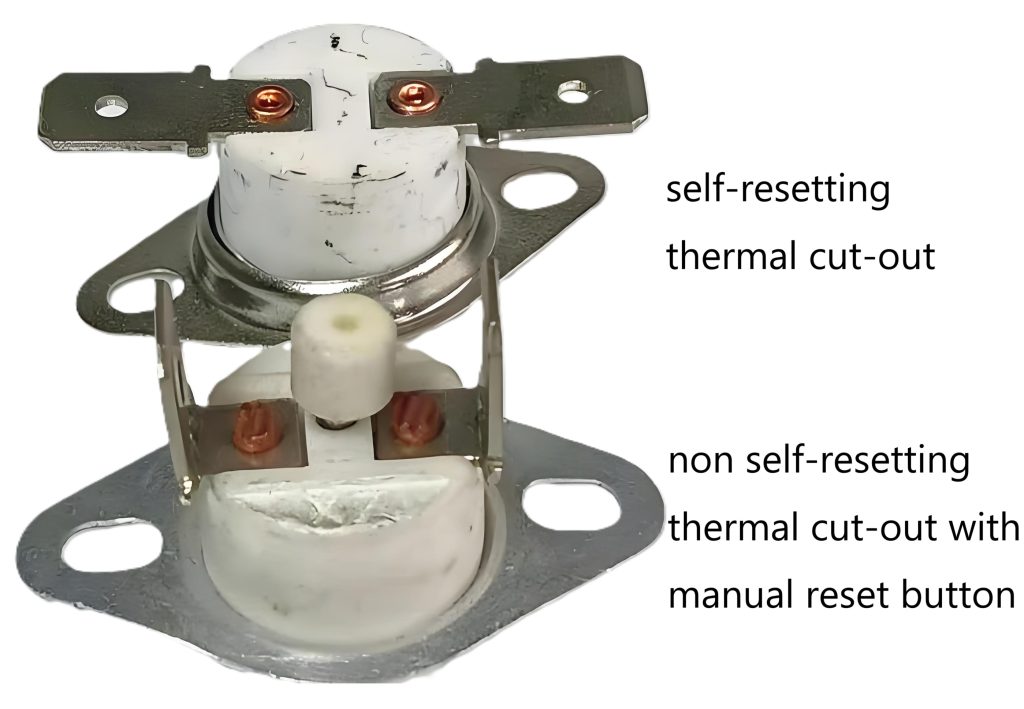
Thermal cut-out is a broad definition, which is subdivided into three categories of thermally sensitive protective devices, namely, self-resetting thermal cut-out, non-self-resetting thermal cut-out, and thermal link.
In normal operation, the component that operates may be a thermostat or temperature limiter, while in abnormal operation the component that operates is a thermal cut-out or a protective device.