8.1.5 What exactly does it protect against?
8.1.5 Live parts of built-in appliances, fixed appliances, and appliances delivered in separate units shall be protected by at least basic insulation before installation or assembly. Compliance is checked by inspection and the test in 8.1.1.
Why is this requirement in place? I believe there are three types of hazards that require protection.
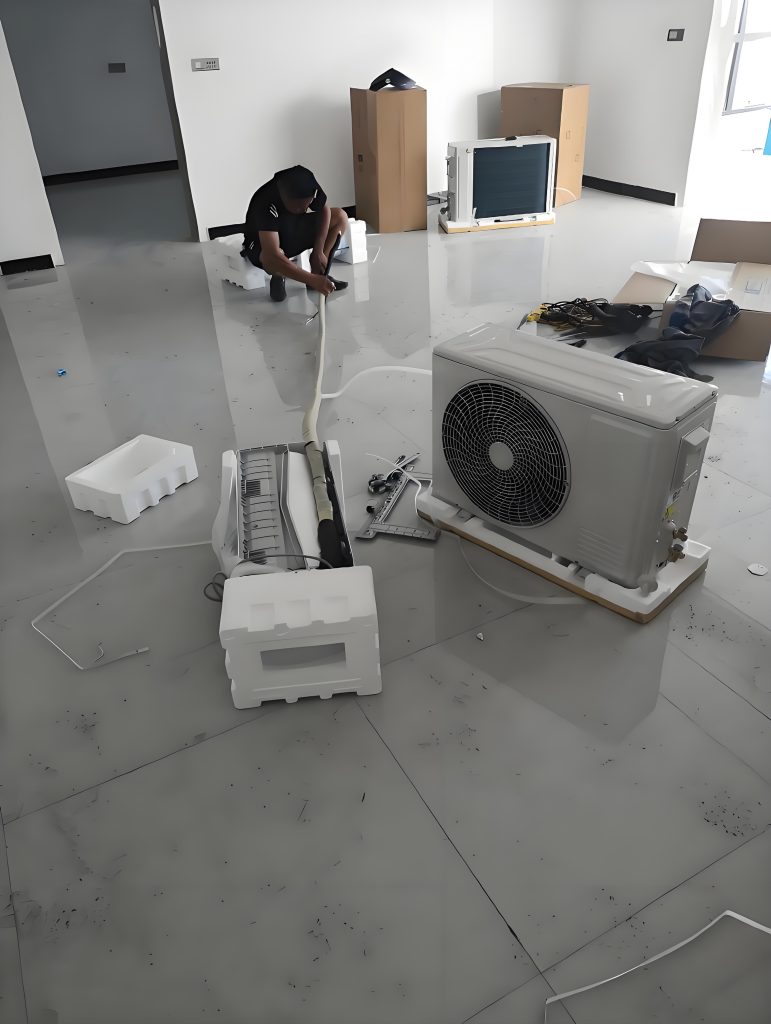
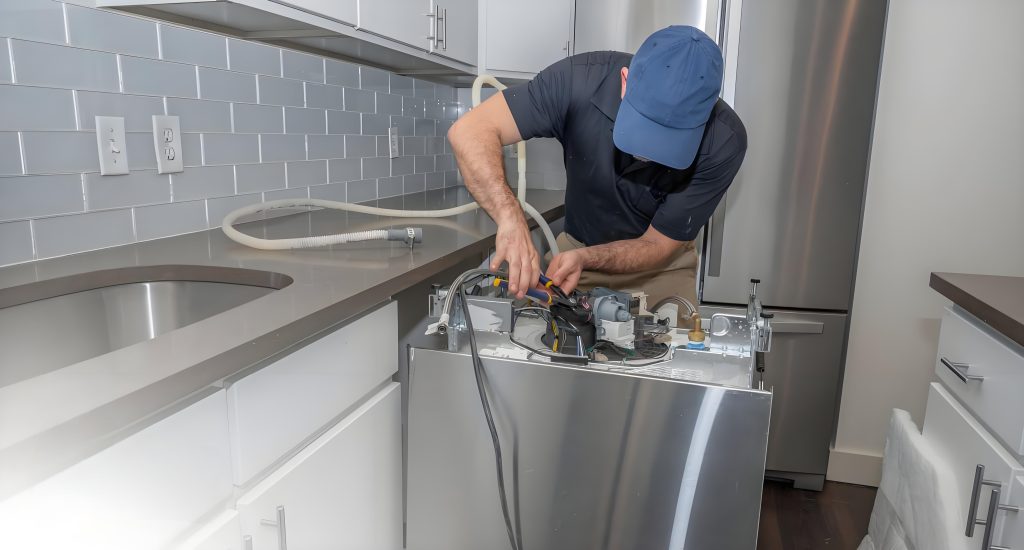
The first is an example of a built-in appliance, such as a dishwashing machine or a tableware sterilizer. Generally, after a dishwasher is installed in accordance with the instructions, except for the front surface, which is accessible, the other five surfaces are inaccessible. They are covered or enclosed by the space provided by the installation location, effectively preventing the risk of electric shock. However, during installation, installers typically don’t power on and test the appliance until it’s fully installed. For built-in products, installers typically power on the appliance to test its operation before placing it in its fixed location. In this case, the appliance isn’t protected from its surroundings, specifically the space where it’s installed. Imagine a scenario where, after unpacking the appliance at the user’s home, some terminals or wires are exposed. This creates a risk of accidental electric shock during installation. Therefore, the standard requires basic insulation protection before installation. To ensure effective basic insulation, we need to apply the test requirements in clause 8.1.1. Implementing the test requirements in clause 8.1.1 inevitably involves clause 22.11 and its definition of removable parts.
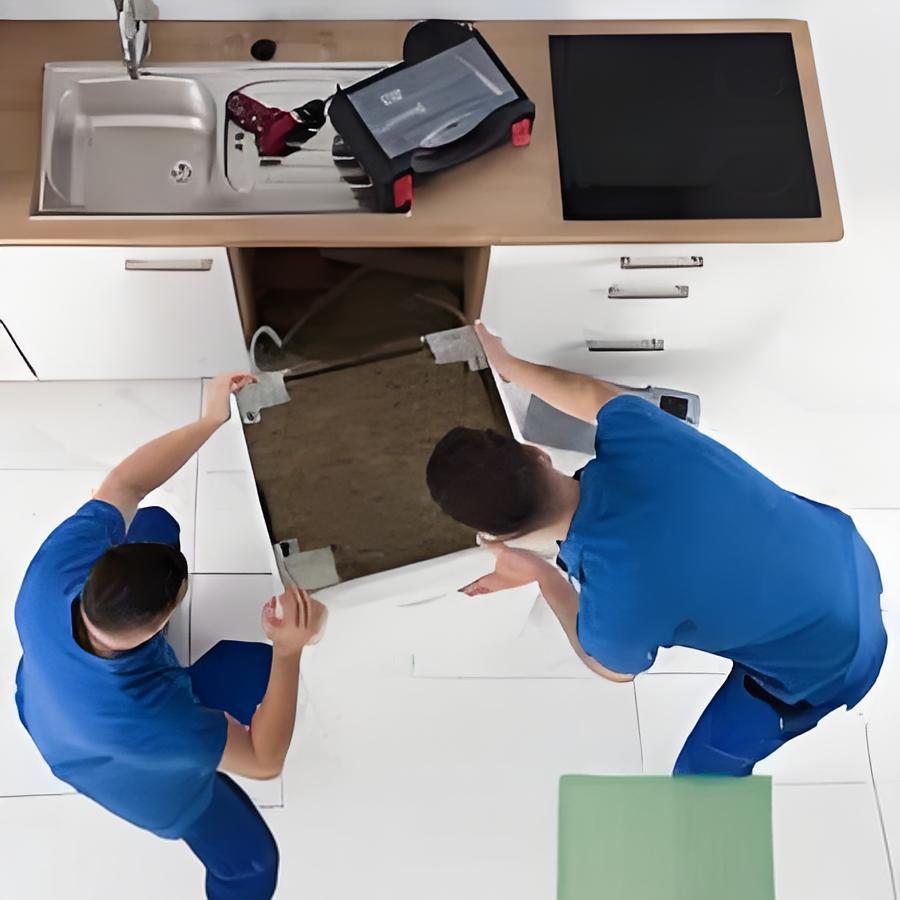


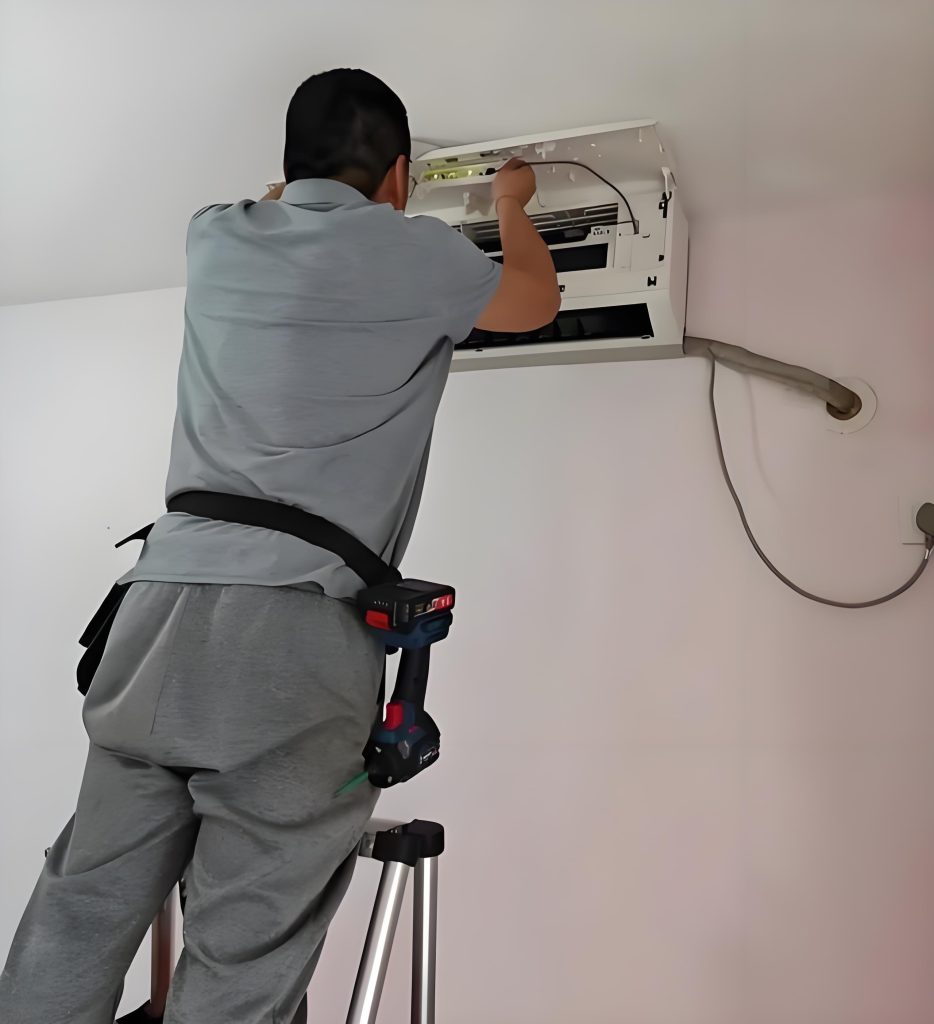
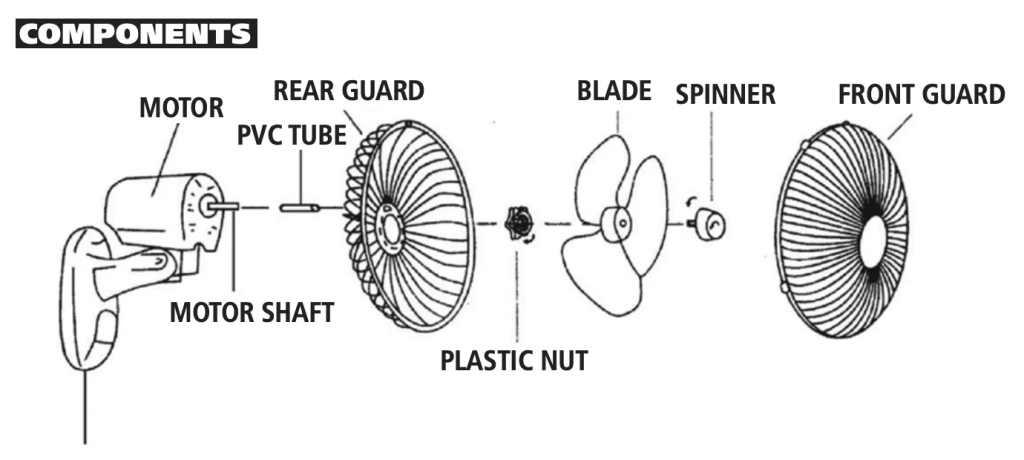
The second type, similar to the first, applies to fixed appliances, such as wall-mounted fans. These products are typically installed on-site and require the installation of a mounting plate or bracket. However, experienced installers will typically verify that the product is functioning properly before proceeding. During the power-on test run, the mounting surface is often not secured to the wall, rendering the wall ineffective. If the mounting surface has a large opening, allowing a finger to penetrate and contact live components, there is a risk of electric shock.
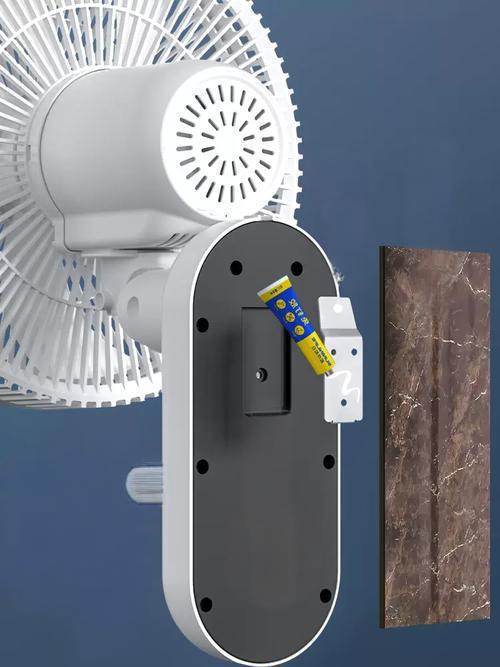
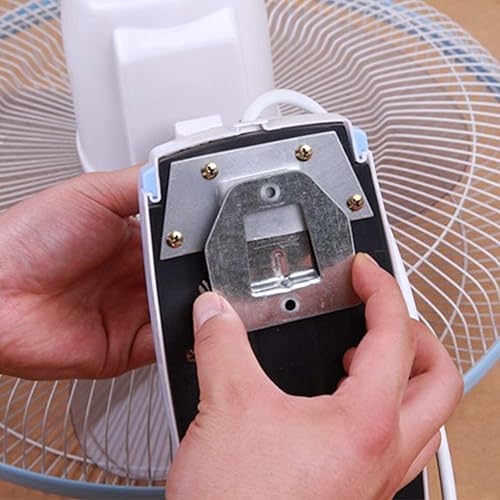



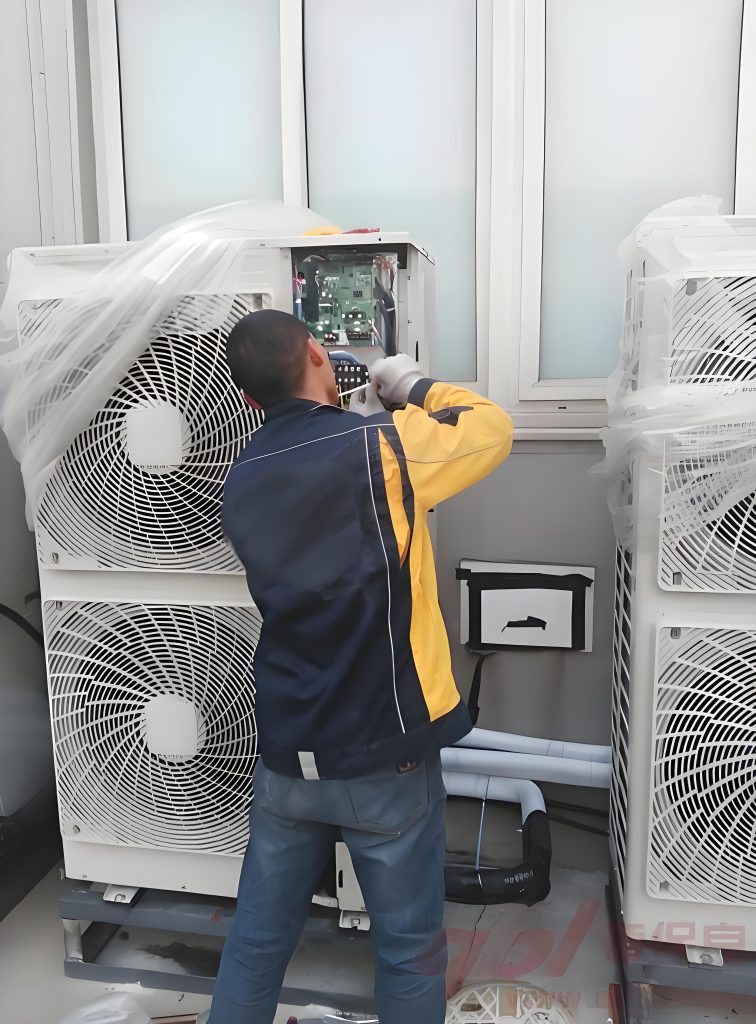
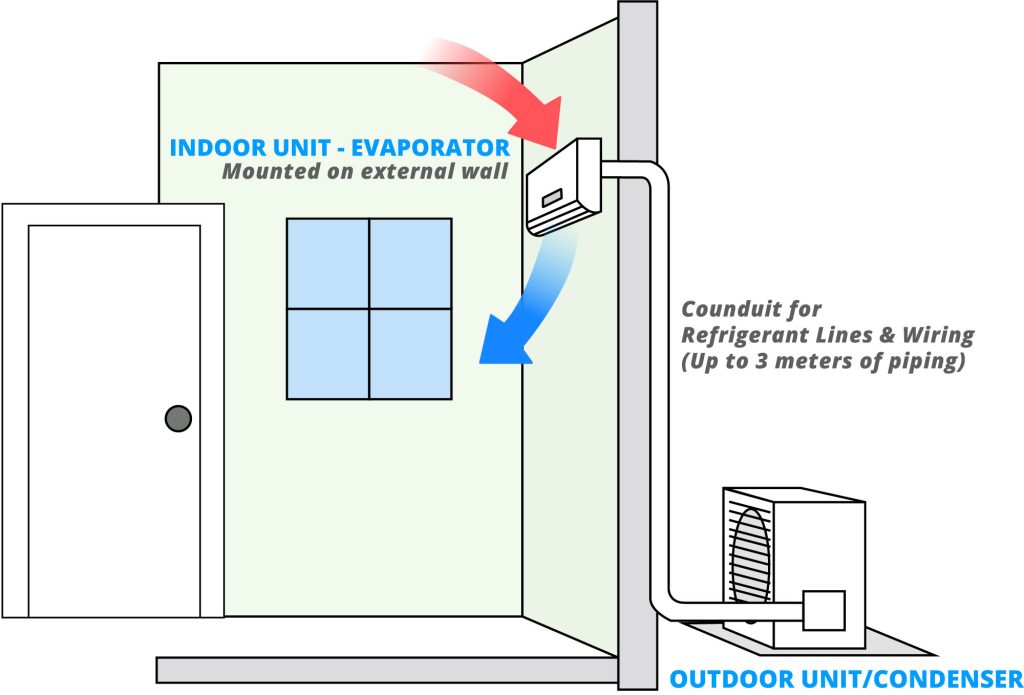
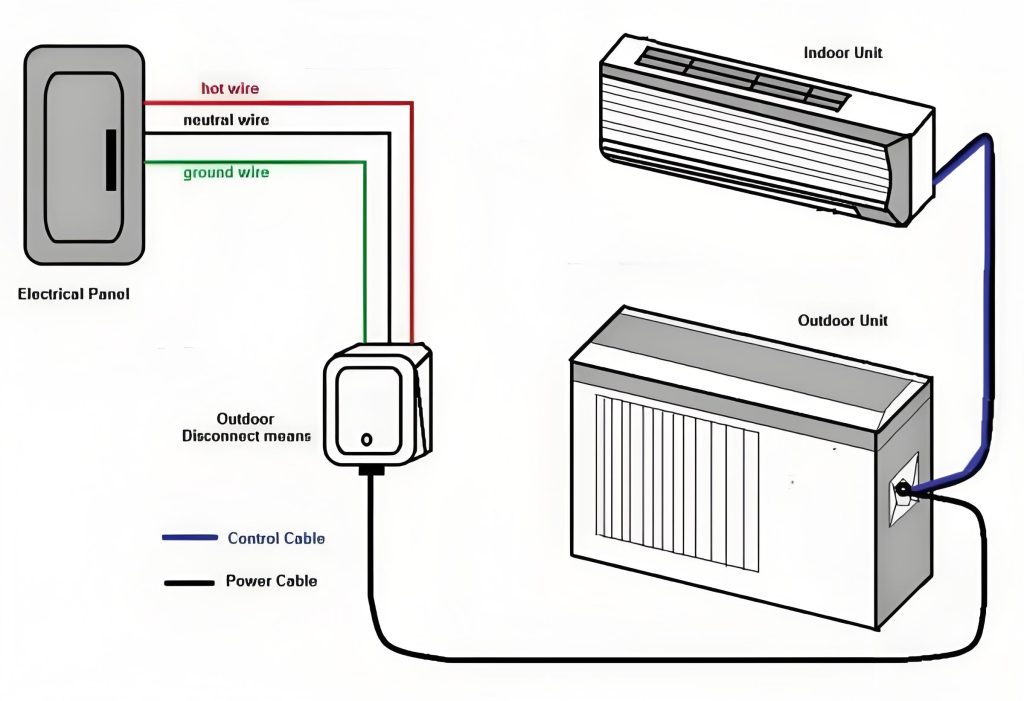
The third type is controversial. Split-type household air conditioners are typically delivered as separate, independent units. These products typically require on-site installation. During installation, is it possible that the outdoor unit has already been installed and connected to the mains power supply? The indoor unit installer is not the same person as the outdoor unit installer and is unaware of the outdoor unit’s installation progress. He or she needs to complete the wiring for both units, potentially completing the wiring while the outdoor unit is energized. A typical wiring task involves connecting the indoor and outdoor unit interconnecting cables. As described in the second scenario, both indoor and outdoor unit wiring terminals require basic insulation protection. However, does the separately delivered interconnecting cable also require basic insulation protection? Note that the interconnecting cables used here all comply with clause 25.23. They all have insulating sheaths, but may have exposed conductors at their ends. The basic insulation protection we will discuss below applies to these exposed conductors. If the standard is strictly adhered to, I believe requiring basic insulation is acceptable. However, in actual production and manufacturing, it is difficult to achieve, and even if it is, the cost is considerable. Therefore, I personally believe that separately delivered interconnecting cables do not require additional basic insulation protection.