Clause 3 – How to understand the definition of “non-self-resetting thermal cut-out”
non-self-resetting-thermal cut-out: thermal cut-out that requires a manual operation for resetting, or replacement of a part, in order to restore the current.
NOTE Manual operation includes disconnection of the appliance from the supply mains.
The thermal cut-out is equipped with a temperature-sensitive component, typically a bimetallic strip or a thermistor, which reacts to heat. As the temperature of the appliance or circuit increases, the bimetallic strip bends or the resistance of the thermistor changes. When the heat decreases and the temperature drops, the bimetallic strip will deform, reconnecting the circuit and completing the self-resetting action. The non- self-resetting thermal cut-out we are discussing here can be reset, but it cannot perform the reset action by itself.
For example, a non-self-resetting thermal cut-out that needs to be reset manually requires pressing a button. I won’t explain how this works here, you can google it yourself.
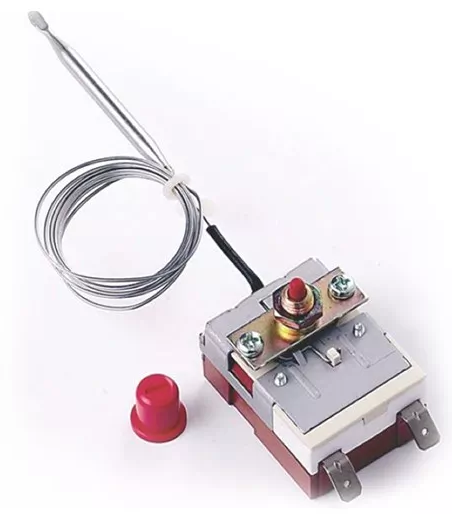
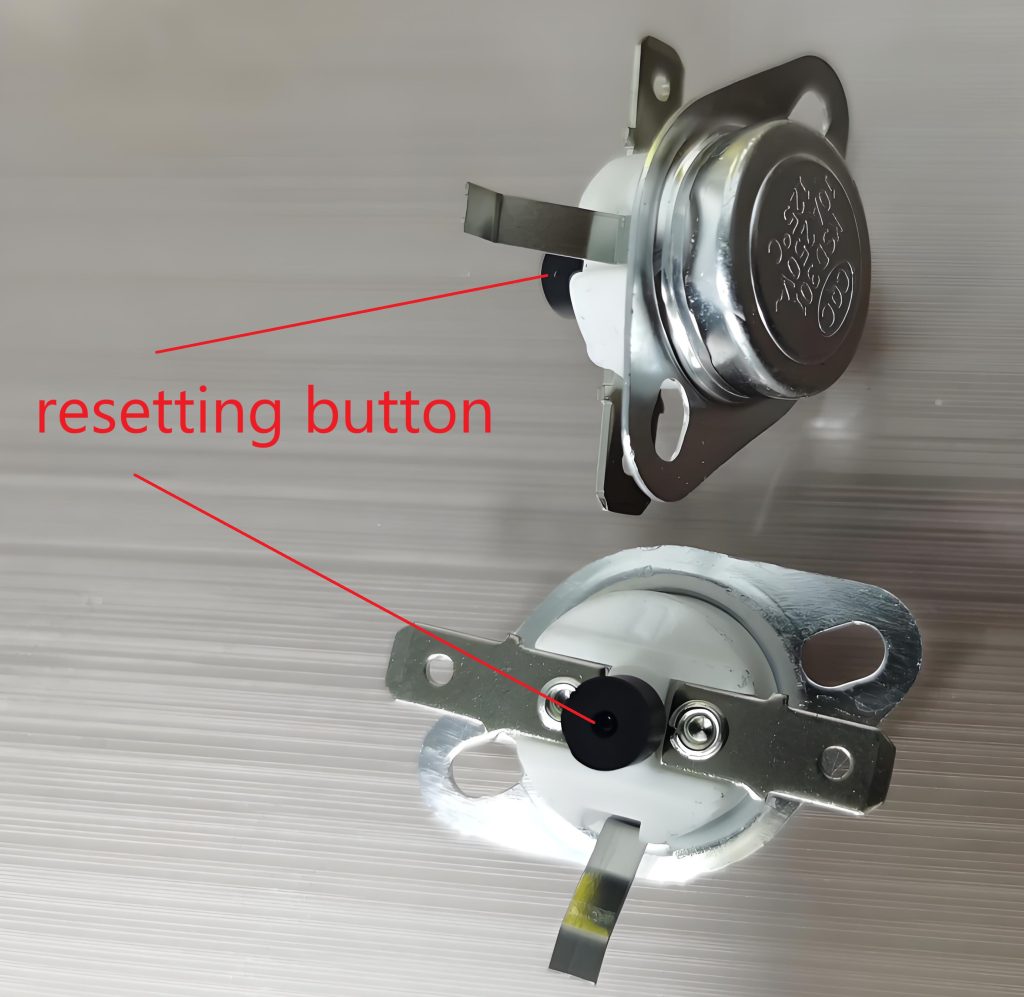
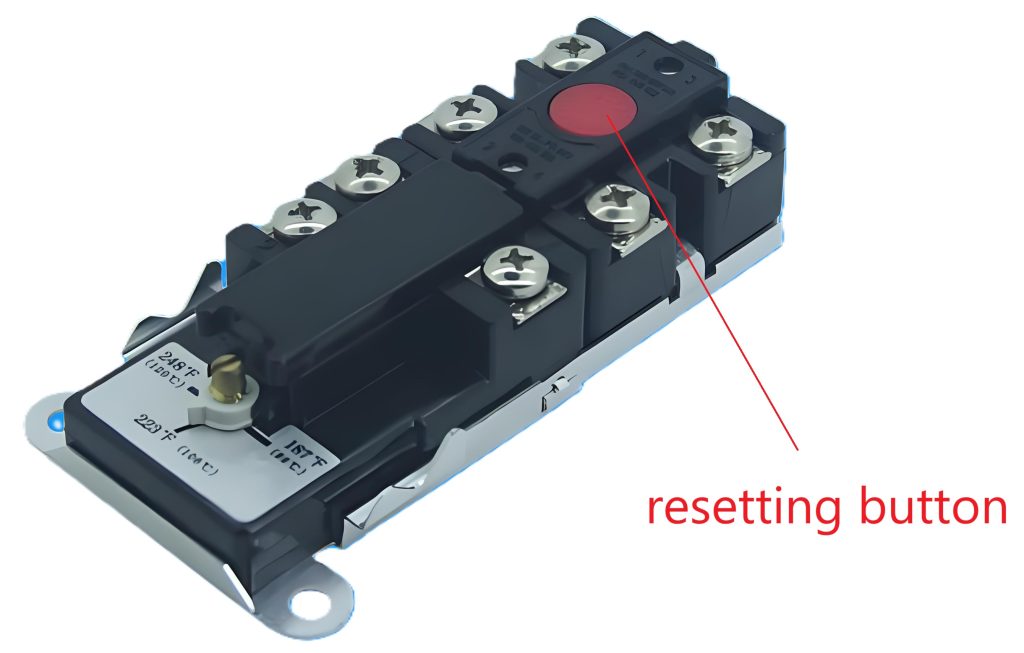
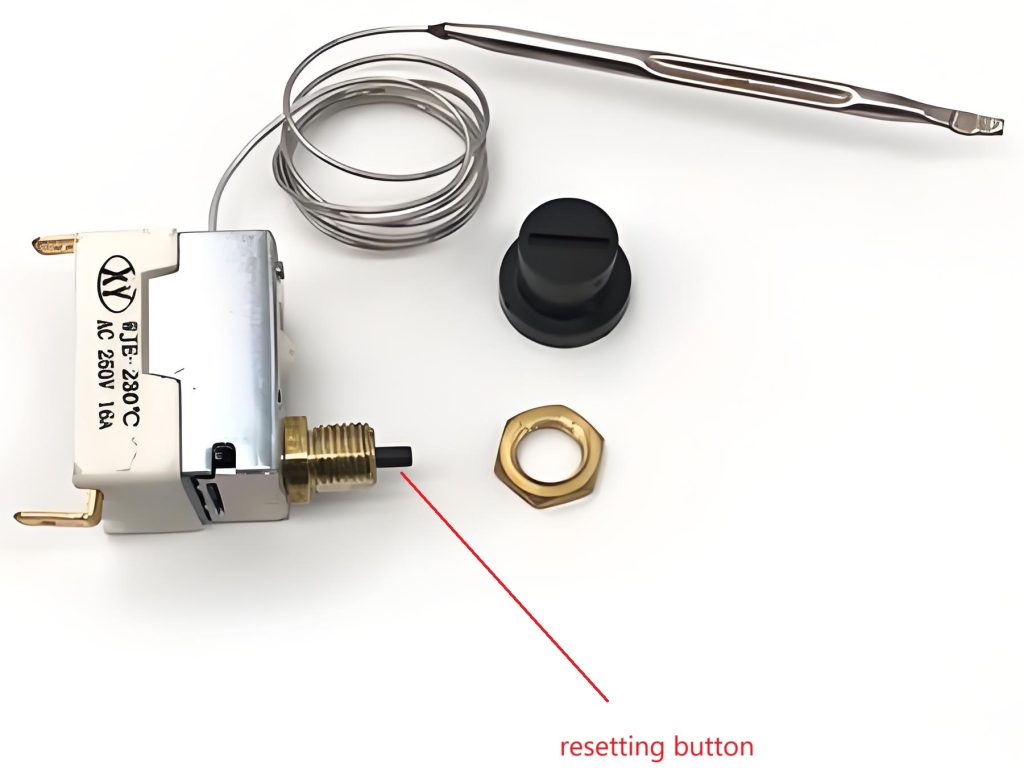



Another type of thermal cut-out is the one that needs to be disconnected from the power/main supply in order to complete the resetting action. Typical non-self-resetting thermal cut-outs(voltage maintained non-self-resetting thermal cut-out) are used in motors and are shown in the figure below:
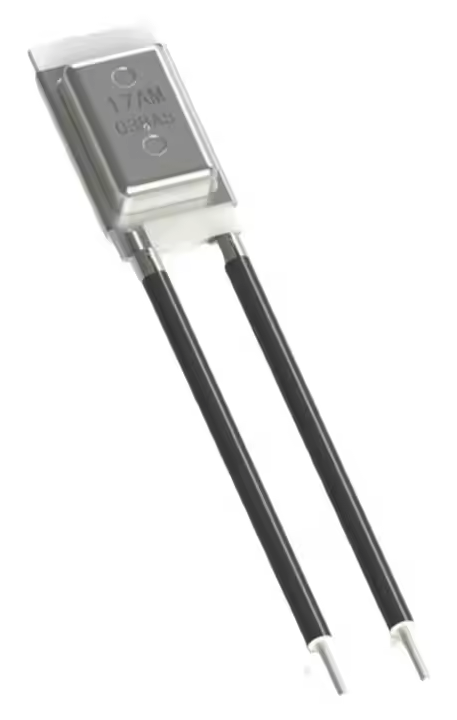

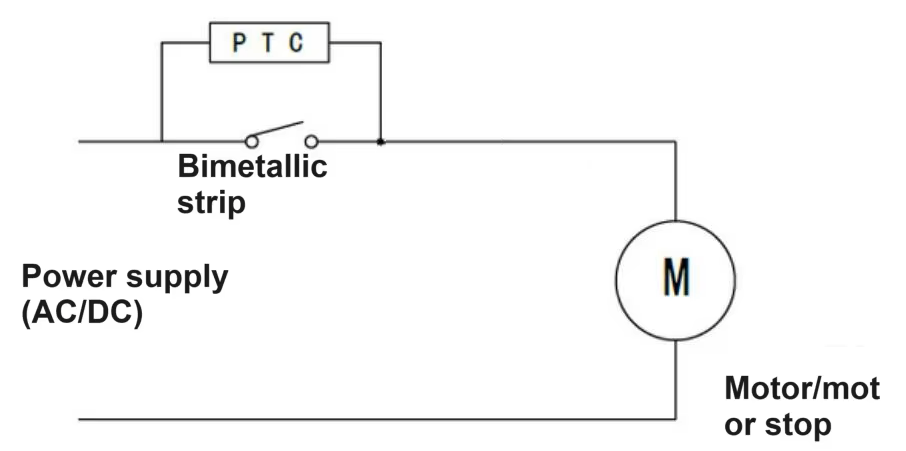
Its working principle can be explained by the figure below. When the bimetallic strip disconnects the circuit, since the PTC is connected to the circuit and is generating heat still, the bimetallic strip is still in a relatively hot state and cannot be reset. When the power is disconnected (for example, the plug is unplugged), the PTC does not generate heat and can be reset after a period of time.
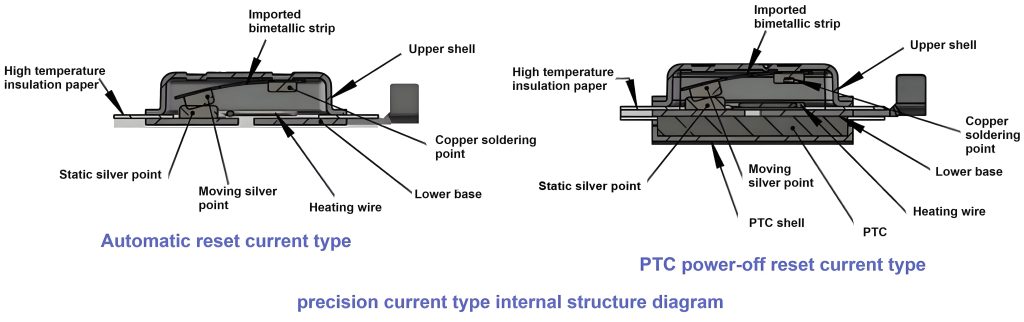
Its internal structure is shown below:
Another voltage maintained non-self-resetting thermal cut-out are used in room heater or hair dryer are shown in the figure below:
