Clause 3 – How to Understand the Definition of “visibly glowing heating element”
visibly glowing heating element: heating element that is partly or completely visible from the outside of the appliance and has a temperature of at least 650 °C when the appliance has been operated under normal operation at rated power input until steady conditions have been established.
The heating element needs to be able to emit light and the light needs to be visible, it is also required that the temperature of the heating element exceeds 650°C. Often when measuring temperature, we measure the temperature at the hottest location, for example, getting the temperature at the surface of a heating element. When testing, please note that it is important to use a thermocouple that is resistant to high temperatures and also to ensure that the calibrated temperature range of the thermocouple covers the temperature being tested.
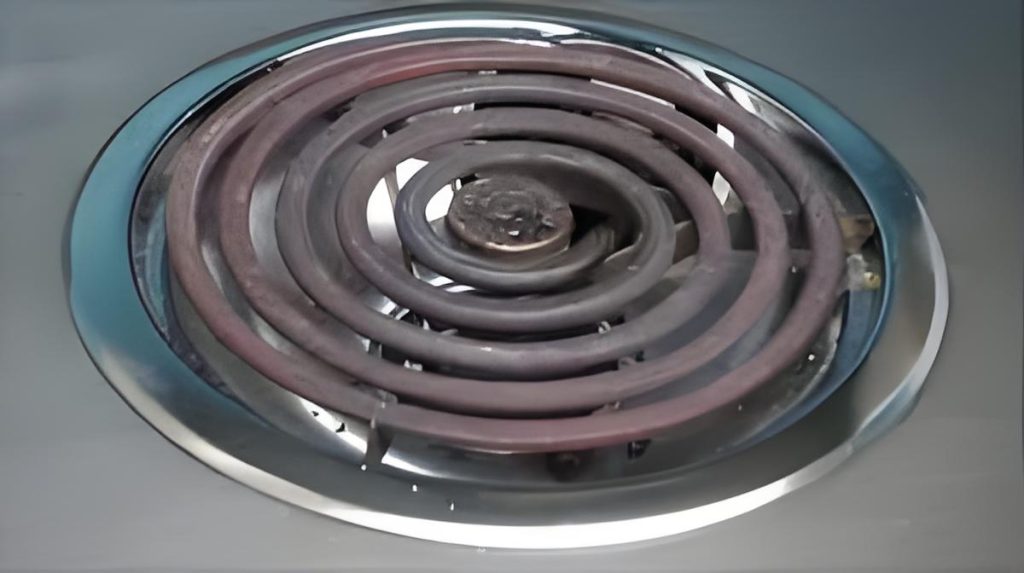
If you have done the clause 30.2 glow wire test then you should have experience that at 650°C the glow wire is non-luminous and only at 750°C does it emit a dim light. Of course, the luminous properties of heating elements may be different from those of a glow wire. Here are some photos of a typical visibly glowing heating element.
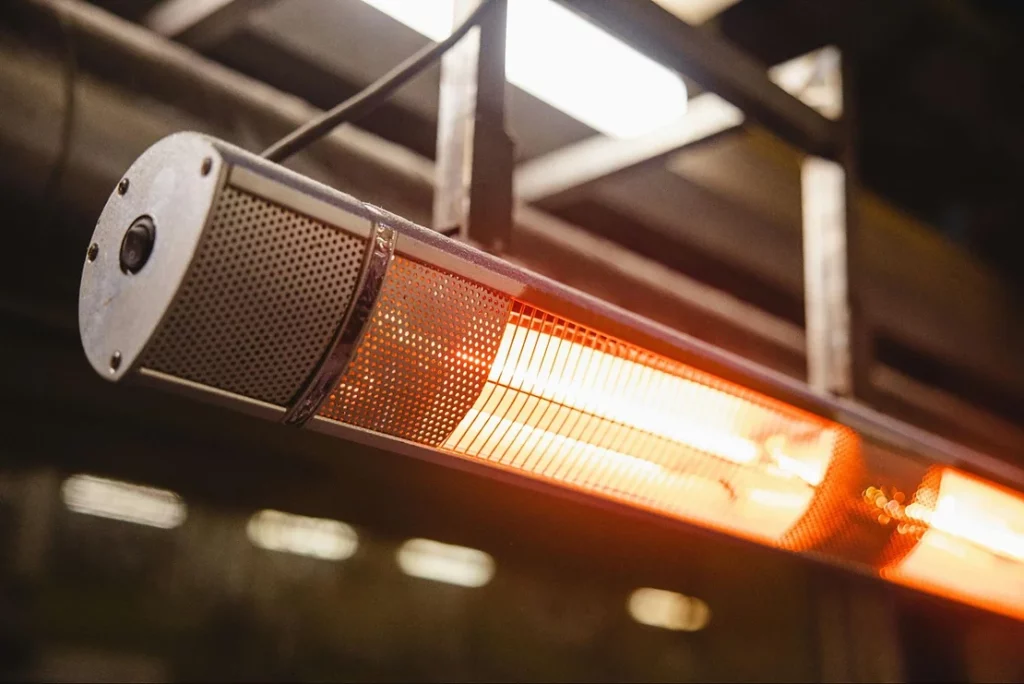

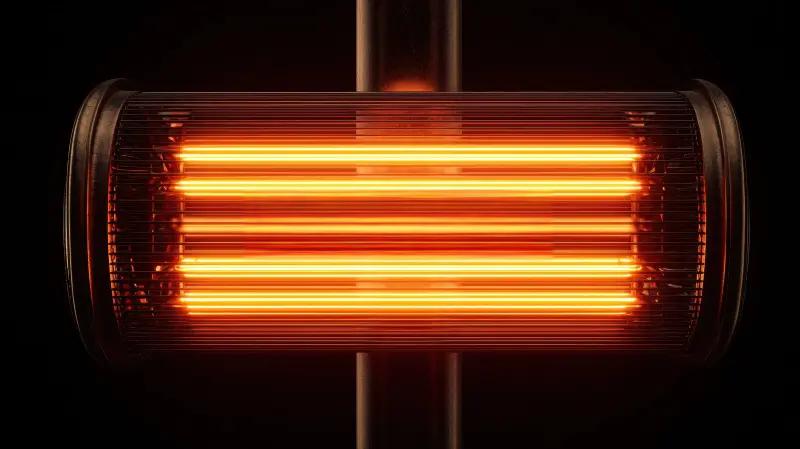

This visibly glowing heating element is a warning to the user of the product, and therefore the test requirements are a little more lenient during the subsequent clause of the test.
There are some glowing heating elements that emit light that is not particularly bright, but as long as they emit light and the temperature exceeds 650°C, they can also be defined as visibly glowing heating elements. However, the two photos below show heating elements that, in my experience, should not be considered as visibly glowing heating elements, as the brightness of the heating elements shown in the photos does not correspond to a temperature of 650°C.

