ข้อ 3 – จะเข้าใจคำจำกัดความของ “ฉนวนเสริม” ได้อย่างไร
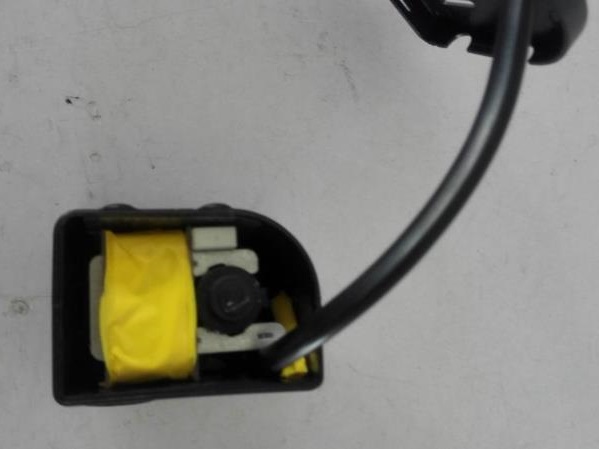
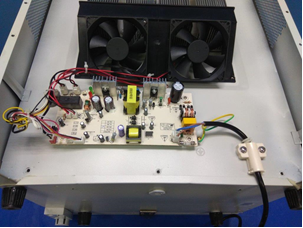
ดังแสดงในสองภาพด้านล่าง ภาพซ้ายเป็นภาพด้านหลังตู้เย็น แผงวงจรด้านในสามารถมองเห็นได้ผ่านตะแกรงโลหะในภาพด้านซ้าย และภาพภายในคือภาพด้านขวา มีส่วนที่มีกระแสไฟฟ้าอยู่บน PCB และผู้ใช้สามารถสัมผัสกระจังหน้าได้ อากาศระหว่างช่องว่างของกระจังหน้าและชิ้นส่วนที่มีไฟฟ้าบนแผงวงจรอาจทำให้เกิดวงจรนำไฟฟ้าได้ ดังนั้นระยะนี้สามารถกำหนดเป็นระยะห่างด้วยฉนวนเสริมได้ เพราะการกวาดล้างและ nbsp; และ nbsp;ประกอบด้วยห่วงอากาศ ห่วงอากาศไม่สามารถแยกออกได้ และเราไม่รู้ด้วยซ้ำว่าจะแบ่งอากาศนี้ออกเป็นหลายส่วนที่ไหน ที่นี่ต้องสังเกตสองประเด็น ถ้าตะแกรงโลหะไม่ได้ต่อสายดิน อากาศระหว่างตะแกรงและชิ้นส่วนที่มีไฟฟ้าในแผงวงจรต้องเป็นไปตามข้อกำหนดของฉนวนเสริม (ตามข้อกำหนดในข้อ 8.2 สำหรับเครื่องใช้ไฟฟ้าประเภท II) ถ้าตะแกรงโลหะต่อสายดิน ดังนั้นอากาศระหว่างตะแกรงและชิ้นส่วนที่มีกระแสไฟฟ้าในแผงวงจรจะต้องเป็นไปตามข้อกำหนดของฉนวนพื้นฐานเท่านั้น เนื่องจากฉนวนพื้นฐานพร้อมสายดินเป็นอุปกรณ์ Class I ที่มีมาตรการป้องกันสองชั้น และผู้ใช้สามารถสัมผัสชิ้นส่วนโลหะที่ต่อสายดินได้
ปั๊มจุ่มที่แสดงด้านล่างมีโพลมอเตอร์สีเทาอยู่ภายใน โดยมีขดลวดหุ้มด้วยฉนวนสีเหลือง เพื่อป้องกันความเสียหายจากน้ำ สเตเตอร์ของมอเตอร์ทั้งหมดจึงถูกห่อด้วยอีพอกซีเรซิน หลังจากที่พันขดลวดแล้ว จะไม่สามารถทดสอบฉนวนพื้นฐานและฉนวนเสริมได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ ก่อนที่จะเทอีพอกซีเรซิน ฉนวนสีเหลืองถือได้ว่าเป็นฉนวนพื้นฐาน และอีพอกซีเรซินถือได้ว่าเป็นฉนวนเสริม อย่างไรก็ตาม เมื่อเทอีพอกซีเรซินลงในตัวเรือนปั๊ม มันจะยึดติดกับวัสดุฉนวนสีเหลืองอย่างแน่นหนา และไม่สามารถแยกวัสดุทั้งสองออกเพื่อการประเมินได้ เช่น การประเมินการทดสอบความแข็งแรงทางไฟฟ้า ดังนั้นฉนวนเสริมจึงถูกสร้างขึ้นตั้งแต่ขดลวดปั๊มไปจนถึงพื้นผิวอีพอกซีเรซินที่สามารถเข้าถึงได้จากภายนอก
As shown in the two pictures below, the left picture is a photo of the back of a refrigerator. The circuit board inside can be seen through the metal grille in the left picture, and the internal photo is the right picture. There are live parts on the PCB, and the user can touch the grille. The air between the gap of the grille and the live parts on the circuit board can form a conductive loop. Therefore, this distance can be determined as an clearance with reinforced insulation. Because the clearance is composed of an air loop, the air loop cannot be separated, and we don’t even know where to divide this air into several parts. Here, two points need to be noted. If the metal grille is not grounded, the air between the grille and the live parts in the circuit board needs to meet the requirements of reinforced insulation (according to the requirements of clause 8.2 for class II appliance), if the metal grille is grounded, then the air between the grille and the live parts in the circuit board only needs to meet the requirements of basic insulation, because basic insulation plus earthing is a class I appliance with double protection measures, and the user can touch the earthing metal parts.

The submersible pump shown below has a shaded pole motor inside, with the windings wrapped in yellow insulation. To prevent water damage, the entire motor stator is wrapped in epoxy resin. After the windings are wrapped, it is not possible to effectively test the basic insulation and supplementary insulation. Before the epoxy resin is poured, the yellow insulation can be considered basic insulation and the epoxy resin can be considered supplementary insulation. However, when the epoxy resin is poured into the pump housing, it will adhere to the yellow insulation material very tightly, and the two materials cannot be separated for evaluation, such as evaluating electrical strength tests. Therefore, reinforced insulation is formed from the pump winding to the externally accessible epoxy resin surface.


